Home »
Financial Risk Management In PSA
Navigate financial risk management within PSA for secure project outcomes.
Introduction
In today’s ever-changing economic landscape, businesses of all sizes are facing an increasing number of financial risks. These risks can come in many forms, such as market volatility, interest rate fluctuations, and currency fluctuations. If not properly managed, these risks can have a significant impact on a company’s bottom line.
Financial risk management (FRM) is the process of identifying, assessing, and mitigating financial risks. The goal of FRM is to protect a company’s financial assets and ensure its long-term financial stability.
What is Financial Risk Management?

What is Financial Risk Management?
Financial risk management refers to the process of identifying, assessing, and mitigating potential risks that may impact an organization’s financial stability and growth. It involves the implementation of strategies and measures to minimize the adverse effects of uncertain events on the company’s financial well-being.
The primary objective of financial risk management is to protect the organization’s assets, enhance its ability to generate profits, and ensure long-term sustainability. This is achieved by analyzing various types of risks, such as market volatility, credit defaults, liquidity constraints, and operational inefficiencies. Through comprehensive risk assessment, companies can develop appropriate risk management strategies tailored to their specific needs.
Financial risk management encompasses several key practices, including risk identification, risk measurement, risk monitoring, and risk mitigation. These activities involve utilizing sophisticated financial models, statistical analysis, and expert judgment to quantify and manage risks effectively. The implementation of risk management frameworks and policies helps organizations optimize their risk-return trade-offs, make informed decisions, and adapt to changing market conditions.
Financial risk management is a broad term that encompasses a wide range of activities. These activities can include:
- Identifying and assessing financial risks
- Developing and implementing risk mitigation strategies
- Monitoring and reporting on financial risks
| Identifying and assessing financial risks | This activity involves identifying potential financial risks that an organization may face, such as market risks, credit risks, liquidity risks, or operational risks. Once identified, these risks are assessed to understand their potential impact and likelihood. |
| Developing and implementing risk mitigation strategies | After assessing the risks, organizations develop strategies to mitigate or minimize these risks. These strategies can include diversification of investments, hedging, insurance, establishing contingency plans, and optimizing capital structure. |
| Monitoring and reporting on financial risks | Financial risk management is an ongoing process that requires continuous monitoring of identified risks and the effectiveness of mitigation strategies. Regular reporting ensures that stakeholders are informed about the organization’s risk exposure and its efforts to manage those risks. |
Types of Financial Risks
One significant type of financial risk is market risk, which encompasses the potential losses resulting from fluctuations in market prices, interest rates, or exchange rates. This risk affects investment portfolios, commodities, and currencies, and can be managed through diversification and hedging strategies.
Credit risk is another critical financial risk, referring to the possibility of default by borrowers or counterparties. It arises when a company fails to repay its debts or honor its contractual obligations. Proper credit assessment, monitoring, and risk mitigation techniques, such as credit limits and collateral requirements, are essential to minimize potential losses.
Lastly, liquidity risk pertains to a company’s ability to meet its short-term financial obligations. Insufficient cash flow or access to liquidity sources can lead to financial distress. Maintaining adequate cash reserves, diversifying funding sources, and implementing robust liquidity management strategies are key to managing this risk.
Understanding and addressing these types of financial risks enables organizations to navigate challenges, protect their financial stability, and promote sustainable growth in the ever-evolving business landscape.
Different types of financial risks
- Market risk: Market risk is the risk that the value of a company’s assets will fluctuate due to changes in market conditions. For example, if the stock market crashes, the value of a company’s stock portfolio could decline significantly.
- Interest rate risk: Interest rate risk is the risk that the cost of borrowing money will increase, which could make it more difficult for a company to repay its debts. For example, if interest rates rise, a company’s interest payments on its loans could increase significantly.
- Currency risk: Currency risk is the risk that the value of a company’s foreign currency assets or liabilities will fluctuate due to changes in exchange rates. For example, if the value of the euro falls against the dollar, a company that has euro-denominated debt could see its debt burden increase significantly.
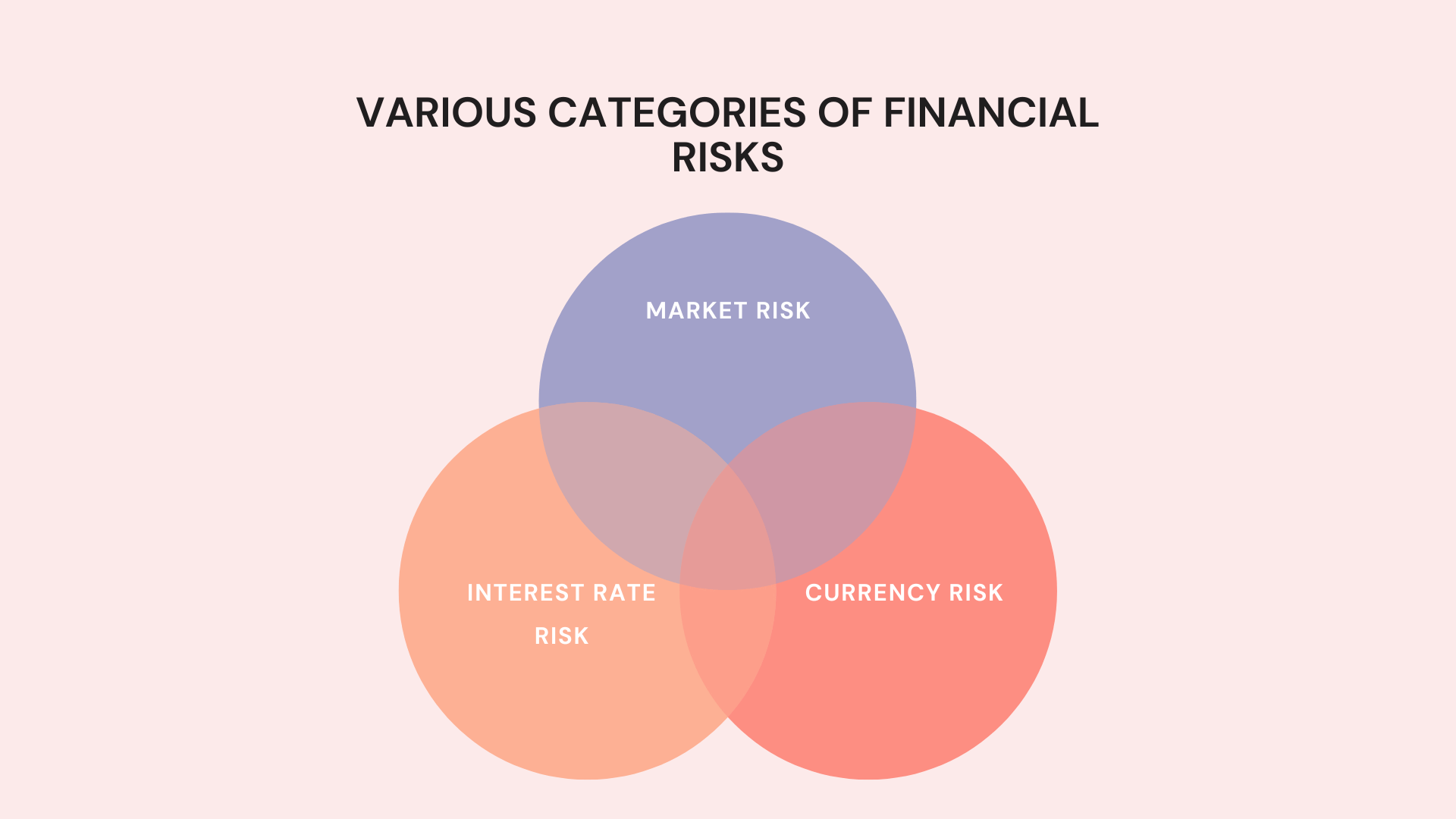
Various Categories of Financial Risks
Advantages of Financial Risk Management
Financial risk management is important for a number of reasons. First, it can help to protect a company’s financial assets. By identifying and assessing financial risks, companies can take steps to mitigate these risks and reduce the likelihood of financial losses.
Second, financial risk management can help to ensure a company’s long-term financial stability. By developing and implementing risk mitigation strategies, companies can reduce their exposure to financial risks and improve their ability to withstand financial shocks.
Third, financial risk management can help to improve a company’s credit rating. A good credit rating can make it easier for a company to borrow money, which can give it a competitive advantage in the marketplace
Importance of Financial Risk Management
- Protection against uncertainties: Financial risk management helps organizations safeguard themselves against unexpected events and uncertainties that can negatively impact their financial stability. By identifying potential risks and implementing appropriate strategies, companies can minimize the impact of adverse events such as market volatility, economic downturns, or regulatory changes.
- Preservation of capital: Effective financial risk management allows businesses to protect their capital and assets. By diversifying investments, monitoring market trends, and employing risk mitigation techniques, organizations can reduce the likelihood of significant financial losses and preserve their capital for sustainable growth.
- Enhanced decision-making: Financial risk management provides valuable insights and analysis that aid in informed decision-making. By assessing various risk factors, organizations can make strategic choices regarding investments, expansion plans, or operational adjustments, resulting in improved performance and profitability.
- Compliance with regulations: Regulatory compliance is a crucial aspect of financial risk management. Organizations must adhere to legal and industry-specific regulations to avoid penalties, reputational damage, and legal consequences. Implementing risk management practices ensures adherence to compliance standards, fostering a trustworthy and responsible image.
- Stakeholder confidence: Financial risk management instills confidence among stakeholders, including investors, shareholders, and creditors. Demonstrating a robust risk management framework portrays the organization as a reliable and responsible entity, attracting investment opportunities, and fostering long-term relationships with stakeholders.
Competitive advantage: Organizations that effectively manage financial risks gain a competitive edge in the market.
| Protection against uncertainties | Financial risk management helps organizations mitigate the impact of unexpected events and uncertainties such as market volatility, economic downturns, or regulatory changes. |
| Preservation of capital | Effective financial risk management safeguards capital and assets by diversifying investments, monitoring market trends, and employing risk mitigation techniques to reduce financial losses. |
| Enhanced decision-making | Financial risk management provides valuable insights and analysis that support informed decision-making. Assessment of risk factors enables strategic choices for investments, expansion, or operational adjustments. |
| Compliance with regulations | Financial risk management ensures adherence to legal and industry regulations. Compliance prevents penalties, reputational damage, and legal consequences, fostering a responsible and trustworthy image. |
| Stakeholder confidence | Financial risk management builds stakeholder confidence by portraying the organization as reliable and responsible. This attracts investments, shareholders, and creditors, fostering long-term relationships. |
| Competitive advantage | Effective financial risk management provides a competitive advantage by positioning organizations as well-prepared and capable of navigating uncertainties, giving them an edge in the market. |
How to Implement Financial Risk Management
- Protection against uncertainties: Financial risk management helps organizations safeguard themselves against unexpected events and uncertainties that can negatively impact their financial stability. By identifying potential risks and implementing appropriate strategies, companies can minimize the impact of adverse events such as market volatility, economic downturns, or regulatory changes.
- Preservation of capital: Effective financial risk management allows businesses to protect their capital and assets. By diversifying investments, monitoring market trends, and employing risk mitigation techniques, organizations can reduce the likelihood of significant financial losses and preserve their capital for sustainable growth.
- Enhanced decision-making: Financial risk management provides valuable insights and analysis that aid in informed decision-making. By assessing various risk factors, organizations can make strategic choices regarding investments, expansion plans, or operational adjustments, resulting in improved performance and profitability.
- Compliance with regulations: Regulatory compliance is a crucial aspect of financial risk management. Organizations must adhere to legal and industry-specific regulations to avoid penalties, reputational damage, and legal consequences. Implementing risk management practices ensures adherence to compliance standards, fostering a trustworthy and responsible image.
- Stakeholder confidence: Financial risk management instills confidence among stakeholders, including investors, shareholders, and creditors. Demonstrating a robust risk management framework portrays the organization as a reliable and responsible entity, attracting investment opportunities, and fostering long-term relationships with stakeholders.
- Competitive advantage: Organizations that effectively manage financial risks gain a competitive edge in the market.
How to Implement Financial Risk Management
There are a number of different ways to implement financial risk management. The specific approach that a company takes will depend on its size, industry, and risk profile. However, there are some general steps that all companies can take to implement financial risk management.
The first step is to identify and assess financial risks. This can be done by conducting a risk assessment, which involves identifying potential risks, assessing the likelihood and impact of these risks, and developing risk mitigation strategies.
The next step is to develop and implement risk mitigation strategies. Risk mitigation strategies can include a variety of activities, such as hedging, diversification, and insurance.
The final step is to monitor and report on financial risks. This involves regularly reviewing the company’s risk profile, identifying new risks, and adjusting risk mitigation strategies as needed.
- Identify and assess risks: Analyze potential financial risks like market volatility, credit risk, liquidity risk, and operational risk.
- Establish risk management objectives: Define goals, such as minimizing losses, regulatory compliance, and financial stability.
- Develop policies and procedures: Create comprehensive guidelines aligned with industry best practices.
- Implement risk measurement tools: Utilize tools like value-at-risk models and stress testing to quantify and evaluate risks.
- Establish risk mitigation strategies: Diversify investments, hedge against risks, and implement internal controls.
- Monitor and review: Continuously evaluate processes, update risk assessments, and adjust strategies as needed.
- Educate and train employees: Foster a risk-aware culture and ensure employees understand their roles.
- Engage external expertise: Consider external consultants or risk management professionals for additional insights.
- Regular reporting and communication: Establish a robust reporting framework for stakeholders.
- Continuously improve: Regularly evaluate and improve the risk management framework to adapt to changing conditions.
Maximize profits with KEBS Finance Management
KEBS – PSA Software helps to maximize productivity through finance management module. The features of Finance Management are:
- MIS – A visual way of tracking the progress of your projects.
- Account payable – Set individual & team project milestones to ensure timely completion of projects.
- Account Receivable – Automate manual tasks to save up more time to execute the critical ones.
- Cash Flow – Make every second count with accurate time tracking.
- Profitability Analysis – Record issues & their solutions to create a comprehensive database for the future projects.
- Consolidation – Plan & execute multiple projects with precision by making data-driven decisions.
- Procurement – Ensure timely completion of milestones with project based timesheets.
- Invoices – Brainstorm with your team even while working remotely to deliver projects with perfection.
- Revenue recognition – Make use of ready-made project templates for swift completion of projects.
- Collector – The Collection Management – Ensure timely completion of milestones with project based timesheets.
- General Ledger – Brainstorm with your team even while working remotely to deliver projects with perfection.
- Cost Accounting – Brainstorm with your team even while working remotely to deliver projects with perfection.
Financial Risk Management In PSA
Conclusion
Financial risk management is an important tool that can help companies to protect their financial assets, ensure their long-term financial stability, and improve their financial performance.
By implementing financial risk management, companies can reduce the likelihood of financial losses, improve their ability to withstand financial shocks, and gain a competitive advantage in the marketplace.
KEBS helps to achieve 2x Growth with your projects and resources.
Contact us to know more!