Home » PSApedia
Cost Performance Index
Understand Cost Performance Index (CPI) for Informed Decision-Making and improve Cost Efficiency
What is Cost Performance Index (CPI)?
The Cost Performance Index (CPI) is a critical metric in project management, representing the efficiency and effectiveness of the monetary resources used in a project. Simply put, it determines how well you are sticking to your budget as your project progresses.
When the CPI is greater than 1, it indicates a favorable cost performance, suggesting the project is under budget. Conversely, a CPI of less than 1 suggests that the project is over budget.
Why is CPI Important?
Understanding CPI is crucial for several reasons:
- Budgetary Control: It allows project managers to track if the project is proceeding within the allocated budget.
- Forecasting: CPI can help in predicting future budgetary needs or identifying potential challenges.
- Stakeholder Communication: A clear understanding of CPI can aid in transparent communication with stakeholders about the project’s financial health.
- Decision Making: Real-time insights into CPI can facilitate proactive decision-making to keep the project on track financially.
Why Cost Performance Index is so important?
Calculating CPI
Formula:
CPI = Earned Value (EV) / Actual Cost (AC)
Where:
Earned Value (EV): The value of the work actually performed.
Actual Cost (AC): The actual costs incurred for the work performed.
Example
Let’s assume for a project, the Earned Value (EV) is $10,000, and the Actual Cost (AC) is $8,000.
Using the formula:
CPI=10,000/8,000=1.25
A CPI of 1.25 indicates the project is performing well concerning the budget.
CPI vs Other Performance Metrics
CPI, while vital, is one of many performance metrics. For instance, the Schedule Performance Index (SPI) focuses on the project’s time efficiency. While CPI tells us how well we are adhering to our budget, SPI indicates how well we are sticking to our timeline. When used together, these metrics provide a comprehensive view of a project’s overall health.
For organizations keen on streamlining business operations and ensuring efficiency, understanding the difference between such metrics becomes paramount. One can delve deeper into this by exploring how different metrics impact organizational performance.
| Performance Metric | Description | Relevance to PSA |
|---|---|---|
| CPI (Cost Performance Index) | Ratio of earned value to actual cost. CPI = EV/AC. A CPI > 1 indicates cost efficiency; a CPI < 1 indicates cost inefficiency. | Measures how effectively the budget is being utilized in projects. Indicates if the project is under or over the budget. |
| SPI (Schedule Performance Index) | Ratio of earned value to planned value. SPI = EV/PV. An SPI > 1 indicates ahead of schedule; SPI < 1 indicates a delay. | Assesses if the project is on schedule. Useful to manage timelines and resource allocation. |
| CV (Cost Variance) | Difference between earned value and actual cost. CV = EV – AC. A positive CV indicates under budget; negative CV indicates over budget. | Indicates the budgetary performance at a specific point in time. Provides insight into cost overruns or savings. |
| SV (Schedule Variance) | Difference between earned value and planned value. SV = EV – PV. A positive SV indicates ahead of schedule; negative SV indicates a delay. | Indicates the schedule performance at a specific point in time. Helps identify potential delays or advances. |
Applications of CPI
While CPI is universally applicable across various projects, its importance escalates in sectors where budget constraints are stringent. For instance:
- Resource Management: By linking CPI with resource allocation strategies, organizations can maximize the ROI of their human resources. Delving deeper into effective resource management provides more insights.
- Financial Planning: Projects with significant financial implications, especially those in the realm of Professional Service Automation (PSA), use CPI as a beacon for steering the project’s financial direction.
- Stakeholder Reporting: For projects with multiple stakeholders, consistent reporting on metrics like CPI can enhance trust and ensure transparent communication.
Ready to Optimize Your CPI?
KEBS, as a robust PSA software, offers tools and features to optimize projects’ CPI:
1. Efficient Cost Tracking: With KEBS finance management features, businesses can monitor project costs in real-time, ensuring they stay within budget.
2. Historical Data Analysis: Analyze past projects, understand their CPI metrics, and leverage these insights for future project planning using KEBS comprehensive analytics.
3. Integrative Approach: KEBS integrates various aspects of PSA, from resource management to deal management, ensuring every facet of a project is optimized for cost efficiency.
4. Timesheet Management: With KEBS timesheet features, companies can ensure that billable hours are efficiently recorded, further optimizing costs.
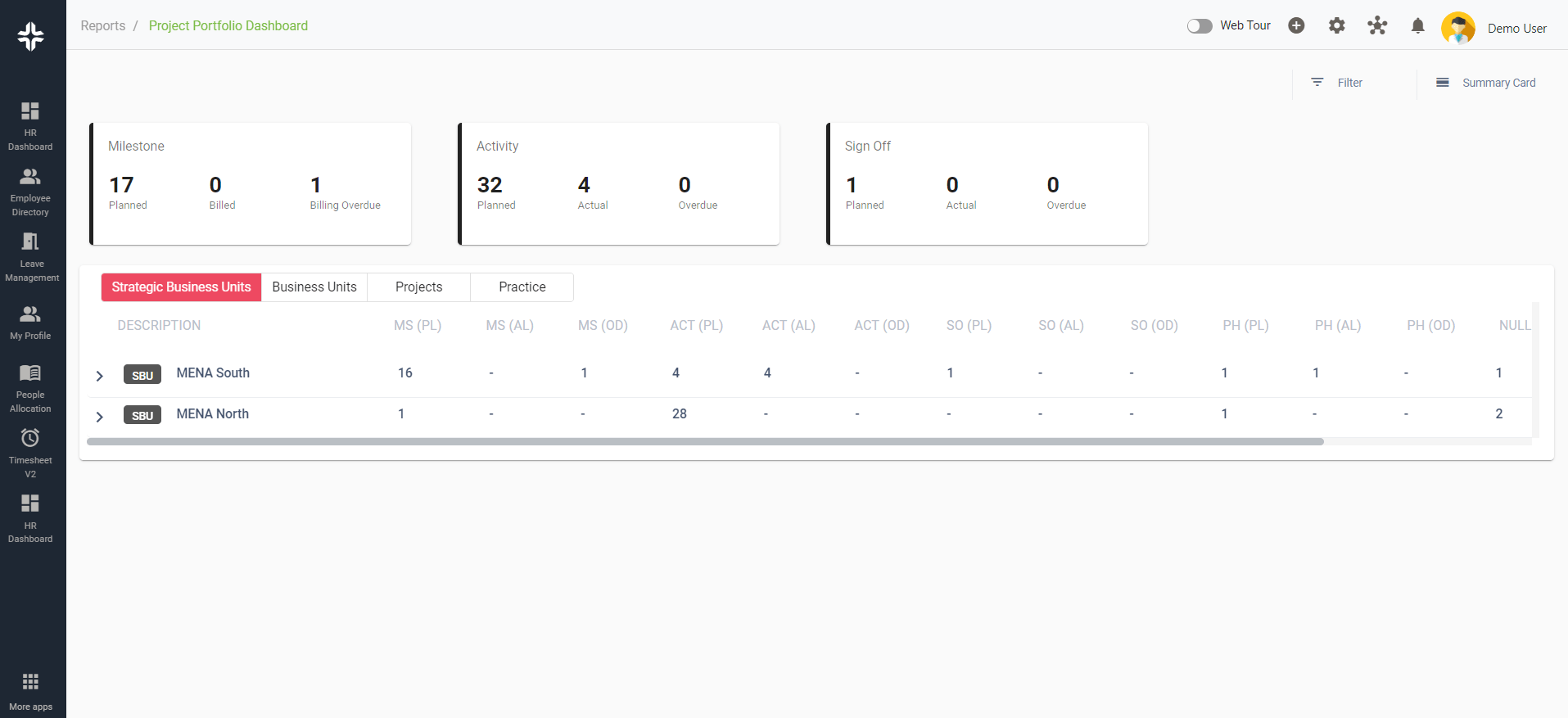
KEBS PMO Dashboard
Ready to unlock the full potential of your projects and optimize your CPI? Dive deep into the world of Professional Service Automation with KEBS’s comprehensive PSA eBook. Alternatively, reach out to our team for more insights or request a live demo to see KEBS in action.



