Home » PSApedia
Cost-to-Income Ratio
Mastering Cost-to-Income Ratios for Sustainable Growth. Learn More about Efficient Financial Management.
What Is Cost-to-Income Ratio?
The Cost-to-Income Ratio (CIR) is a critical financial metric used to assess a company’s efficiency by comparing operating costs to operating income. Essentially, it measures how much a company needs to spend to earn a dollar. The lower the CIR, the more efficient the company’s operations.
The Cost-to-Income Ratio, often used in the banking sector, measures an organization’s operational efficiency. It’s calculated by dividing a company’s operating costs by its operating income. A lower ratio indicates better efficiency, as it means the company is spending less to generate each unit of income. Regular monitoring of this ratio can help businesses understand their operational health and make informed financial decisions. For businesses aiming to optimize financial management and project predictability, understanding CIR is pivotal.
Why Is the Cost-to-Income Ratio Important?
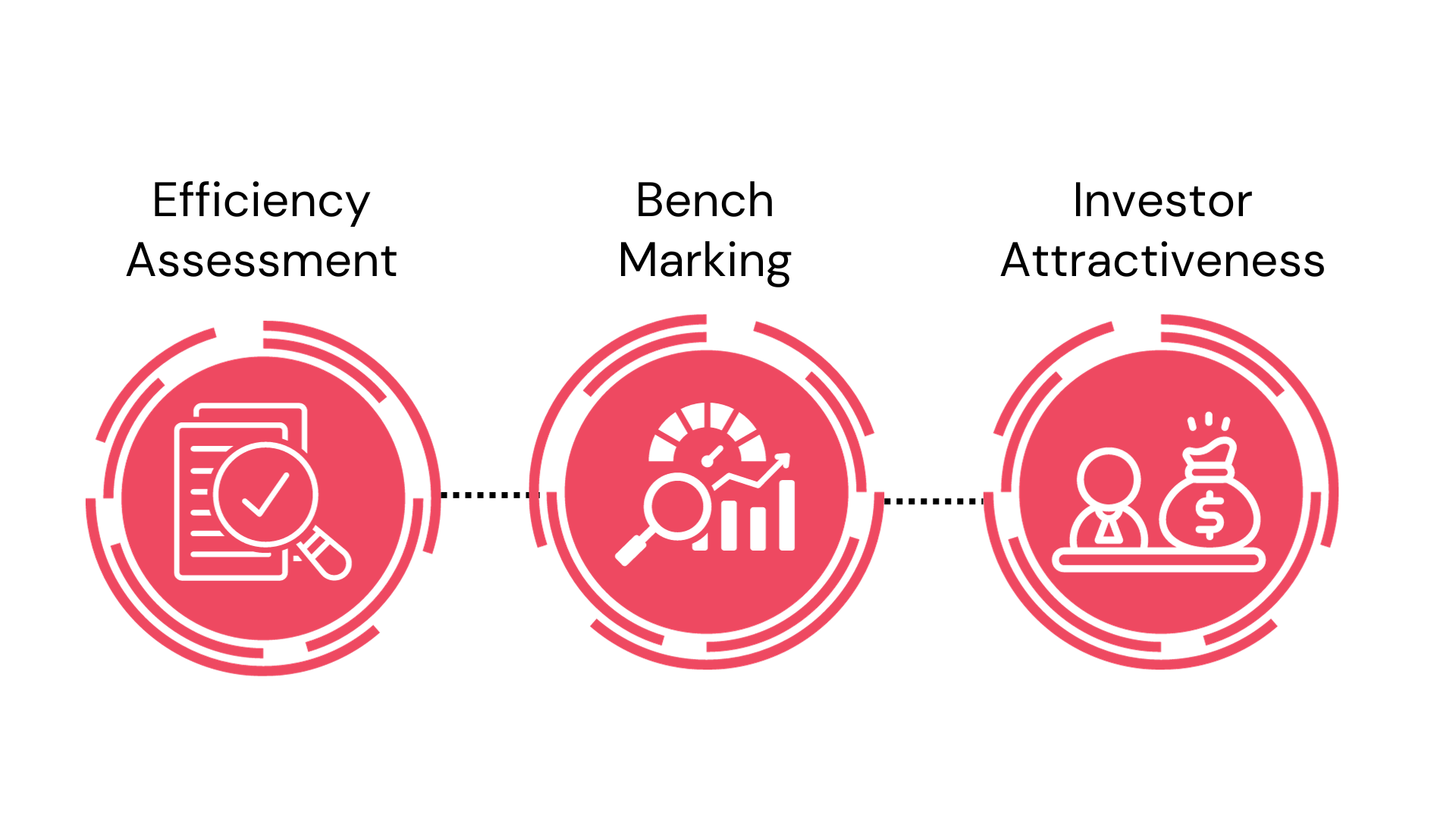
The Cost-to-Income Ratio (CIR) is crucial to PSA because it measures operational efficiency, reflecting the proportion of costs relative to income. A lower CIR indicates better profitability potential, enabling PSA to assess performance and streamline operations. CIR serves multiple purposes:
Efficiency Assessment: Helps in gauging operational efficiency. A lower ratio indicates that the company is more efficient at converting its costs into income.
Benchmarking: Companies often compare their CIR to industry peers to identify areas for improvement or competitive advantages.
Investor Attractiveness: Potential investors often consider CIR as an indicator of a company’s profitability potential.
Why Is the Cost-to-Income Ratio Important?
How to Calculate the Cost-to-Income Ratio?
Formula:
Cost-to-Income Ratio = (Operating Costs / Operating Income) × 100
Example: Let’s consider a hypothetical company, XYZ Corp. If their operating costs for a fiscal year were $500,000 and their operating income was $1,000,000, the CIR would be:
CIR = (500,000 / 1,000,000) × 100 = 50%
This means XYZ Corp. spends 50 cents for every dollar it earns.
Cost-to-Income Ratio vs Other Financial Ratios
While CIR offers insight into operational efficiency, other metrics are vital for a holistic view. For example:
- Gross Profit Margin: Shows the percentage of revenue that exceeds the cost of goods sold.
- Net Profit Margin: Measures how much of each dollar earned by the company is translated into profits.
- By using efficient project financial management, companies can optimize these ratios and drive profitability.
| Financial Ratio | Description | Purpose/Formulation | Commonly Used In |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cost-to-Income Ratio | Measures a company’s costs in relation to its income. | Operating Costs / Operating Income | Banking and financial institutions. |
| Current Ratio | Measures a company’s ability to pay off its short-term liabilities. | Current Assets / Current Liabilities | All sectors to assess liquidity. |
| Debt-to-Equity Ratio | Indicates the proportion of equity and debt a company uses to finance assets. | Total Liabilities / Shareholder’s Equity | All sectors to assess leverage. |
| Gross Profit Margin | Measures the profitability after considering Cost of Goods Sold. | Gross Profit / Sales | All sectors to assess profitability. |
| Return on Assets (ROA) | Shows the profitability of a company relative to its total assets. | Net Income / Average Total Assets | All sectors to assess efficiency. |
| Return on Equity (ROE) | Measures the profitability relative to shareholders’ equity. | Net Income / Shareholder’s Equity | All sectors to assess profitability. |
How Is the Cost-to-Income Ratio Used in Business?
Companies employ the CIR in various ways:
Strategy Formulation: Firms with high CIRs might look into streamlining business processes to improve efficiency.
Resource Allocation: Organizations could adjust resource allocation based on the ratio. For instance, if a particular department has a consistently high CIR, resources might be reallocated or processes reevaluated with the help of resource management software.
Predictability: By maintaining a consistent CIR, companies can improve their “Cost Predictability Index”, making it easier to forecast financial outcomes and optimize fixed-fee projects for success.
Ready to Improve Your Cost Predictability Index?
Achieving a favorable Cost-to-Income Ratio and enhancing your Cost Predictability Index is easier with the right tools. KEBS offers a suite of solutions, from project management to deal management software that aids in improving operational efficiency.
KEBS Finance Management
Are you ready to optimize your financial metrics? Contact us today or get a demo to explore how KEBS can transform your financial management strategies.



