Home » PSApedia
Cost Utilization Rate
Cost Utilization Rate measures resource expenditure against output
What Is Cost Utilization Rate (CUR)?
Cost Utilization Rate (CUR) is a crucial financial metric that measures the efficiency of resource usage in a business. It captures the percentage of the total available resources that are utilized to produce goods or services in a given period. The objective is to maximize the use of resources, minimize waste, and improve profitability.
Cost Utilization Rate (CUR) is a financial metric that measures how efficiently an organization uses its resources. It quantifies the relationship between the actual costs incurred and the budgeted or expected costs for a particular project or period.
Why Is CUR so Important?
UR is a vital component of any business’s financial health. It helps in identifying unused or underutilized resources, which can then be reallocated efficiently. A high CUR indicates that a company is making the most of its available resources, whereas a low CUR may signal inefficiencies or potential areas for improvement.
A CUR below 100% indicates cost savings, as expenses are lower than planned, while a CUR above 100% signifies cost overruns, indicating that expenditures exceed the budgeted amount. CUR helps businesses assess their financial performance and control expenses to stay within budgetary constraints.
Factors affecting CUR
How to Calculate CUR with Formula and Example
Calculating CUR is relatively straightforward. Here’s the formula:
CUR = (Total Used Resources / Total Available Resources) * 100%
For instance, if a business has a total of 1000 units of a resource and has used 800 units, the CUR would be:
CUR = (800 / 1000) * 100%
CUR = 80%
This means the business is utilizing 80% of its resources.
Differences Between CUR and Other Cost Metric
While CUR focuses on the usage efficiency of resources, other cost metrics like the Cost Performance Index (CPI) or Return on Investment (ROI) look at different aspects of financial performance. CPI measures the cost efficiency of budgeted resources, while ROI calculates the return on an investment relative to its cost. Each of these metrics offers unique insights into company performance.
Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC), Customer Lifetime Value (CLV), and Customer Retention Rate (CRR) are key metrics used in marketing and business. CUR (Customer Utilization Rate) differs from these metrics as it focuses on how effectively existing customers are utilizing your product or service, whereas CAC measures the cost of acquiring new customers.
How Is CUR Used?
CUR serves as a key indicator for resource planning and process improvements. It helps businesses understand where they can cut costs, increase efficiency, and allocate resources better. It also provides valuable data for strategic decisions, such as whether to invest in additional resources, outsource certain functions, or improve existing processes.
CLV calculates the total value a customer brings over their lifetime, and CRR tracks the percentage of customers retained over a specific period. CUR helps assess the satisfaction and engagement of your current customer base, while the others primarily deal with customer acquisition, value, and retention.
CUR vs Total Cost vs Annual Cost
While CUR measures resource utilization efficiency, total cost and annual cost are absolute figures that represent the total expenses incurred by a business.
CUR provides a relative measure of efficiency, whereas total cost and annual cost give an absolute measure of expenditure.
| Aspect | CUR (Cost and Usage Report) | Total Cost | Annual Cost |
| Definition | Detailed report of AWS usage and costs, including individual resources and services. | Total expenses incurred for AWS services over a specific period. | Total expenses incurred for AWS services over a 12-month period. |
| Granularity | Granular, can be broken down by service, resource, time period, and more. | Aggregated, provides a single overall cost figure. | Aggregated, provides a total cost over a year, but lacks granularity. |
| Usage Period | Typically monthly, can be customized. | Specific time period (e.g., monthly, quarterly, annually). | Fixed annual timeframe. |
| Use Cases | Detailed cost analysis, budgeting, resource optimization, and chargeback mechanisms. | Quick cost overview, high-level budget tracking. | Annual budgeting, long-term cost planning. |
| Customization | Highly customizable with various report dimensions and filters. | Limited customization, often a summary figure. | Limited customization, typically annual budgets. |
| Frequency of Update | Typically updated daily or at least monthly. | Updated as per your selected reporting period. | Updated annually. |
Optimizing Your CUR with KEBS
With KEBS, a leading PSA software, you can streamline your resource management and improve your Cost Utilization Rate. KEBS provides real-time insights into resource usage, helping you identify underutilized resources and areas for improvement. By leveraging KEBS, you can optimize your CUR, reduce waste, and increase profitability.
Managing your Cost Utilization Rate is crucial for business efficiency and profitability. With tools like KEBS, you can keep a close eye on your CUR and make data-driven decisions that drive your business forward.
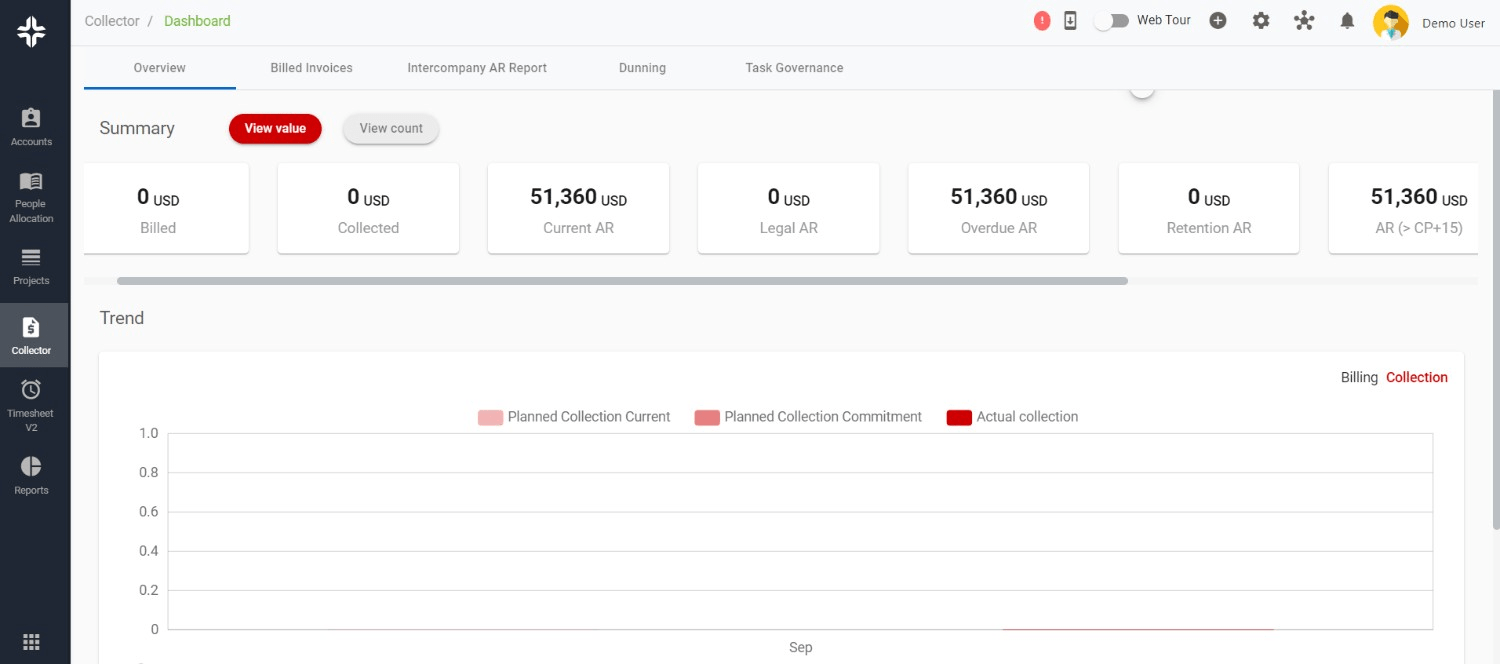
KEBS Collector
Discover the KEBS demo right now. Should you have any inquiries, require support, or wish to connect with KEBS, feel free to contact us.



