Home » PSApedia
Current Accounts Payable Ratio
Understand Your Current Accounts Payable Ratio. Manage Cash Flow Smartly.
What is the Current Accounts Payable (AP) Ratio?
The AP Ratio measures a company’s ability to pay short-term debts with short-term assets. Professional Service Automation (PSA) helps service businesses maintain financial health by ensuring they have sufficient funds and meet their obligations.
PSA is a tool that assists service businesses in managing their finances effectively. It ensures that these businesses have enough money to operate smoothly and fulfill their financial responsibilities. By using PSA, service businesses can avoid financial difficulties and maintain a stable financial position.
Importance of the Current AP Ratio
Current AP Ratio not only safeguards against liquidity crises but also constructs a resilient financial foundation. In PSA, it helps with resource allocation, strengthens vendor relationships, and ensures smooth service, leading to business success and client satisfaction. In the world of finance, maintaining a healthy AP Ratio is crucial. It ensures:
1. Liquidity: A higher ratio indicates that the company can easily cover its short-term liabilities, ensuring smooth operations.
2. Trustworthiness: Vendors and creditors often look at this ratio to determine a company’s creditworthiness.
3. Operational Efficiency: Within PSA, a balanced AP Ratio indicates efficient resource allocation and financial management.
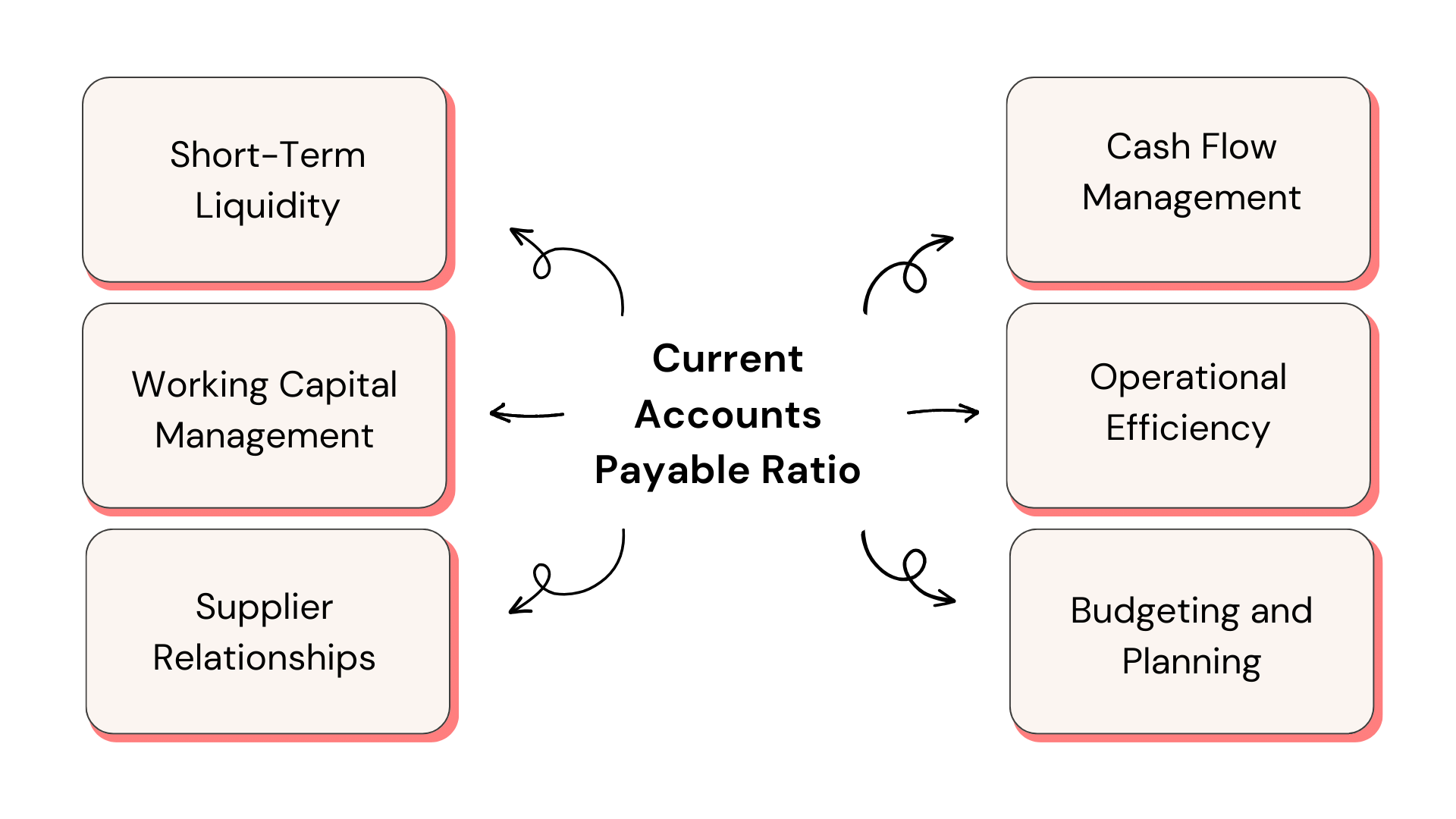
Why Current Accounts Payable Ratio is so important?
How to Calculate the Current AP Ratio?
Formula:
AP Ratio = Accounts Payable / Short – term Assets
Example:
Let’s say a company has accounts payable of $50,000 and short-term assets worth $200,000.
AP Ratio=50,000/200,000=0.25
This means that for every dollar of short-term assets, the company owes 25 cents in accounts payable.
Difference Between AP Ratio and Other Related Metrics
For businesses using project management tools, understanding these differences can help in making informed financial decisions. While the AP Ratio focuses on short-term liabilities, there are other metrics like the Current Ratio and Quick Ratio that also provide insights into a company’s financial health. The main difference is the components they consider:
1. Current Ratio: Considers all current liabilities, not just accounts payable.
2. Quick Ratio: Excludes inventory from short-term assets, providing a more conservative view.
| Metric | Full Name | Definition | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| AP Ratio | Allocation to Pipeline Ratio | Ratio of billable hours allocated to pipeline | Evaluate resource allocation efficiency |
| Utilization Rate | Resource Utilization Rate | Ratio of billable hours to total available hours | Measure resource productivity |
| Billable Ratio | Billable Hours Ratio | Ratio of billable hours to total worked hours | Assess revenue generation efficiency |
How the AP Ratio is Used in Businesses?
In the realm of ticket management, for instance, a healthy AP Ratio ensures that software subscriptions and vendor payments are made on time, ensuring uninterrupted service. The AP Ratio is more than just a number. It’s a tool that businesses, especially those in the PSA sector, use to:
- Assess Financial Health: A low ratio might indicate potential liquidity issues.
- Strategize Payments: Companies can prioritize payments based on their AP Ratio.
- Strengthen Vendor Relationships: By ensuring timely payments, businesses can build trust with vendors.
Ready to Optimize AP Ratio?
Ready to take control of your financial health? With KEBS, optimizing your AP Ratio becomes a breeze. Here’s how:
KEBS offers tools that streamline financial management, ensuring you always have real-time data on your accounts payable and assets. Dive deep into your financials with custom reporting, helping you make informed decisions. Whether it’s resource management or deal management, KEBS ensures all your systems work in harmony.
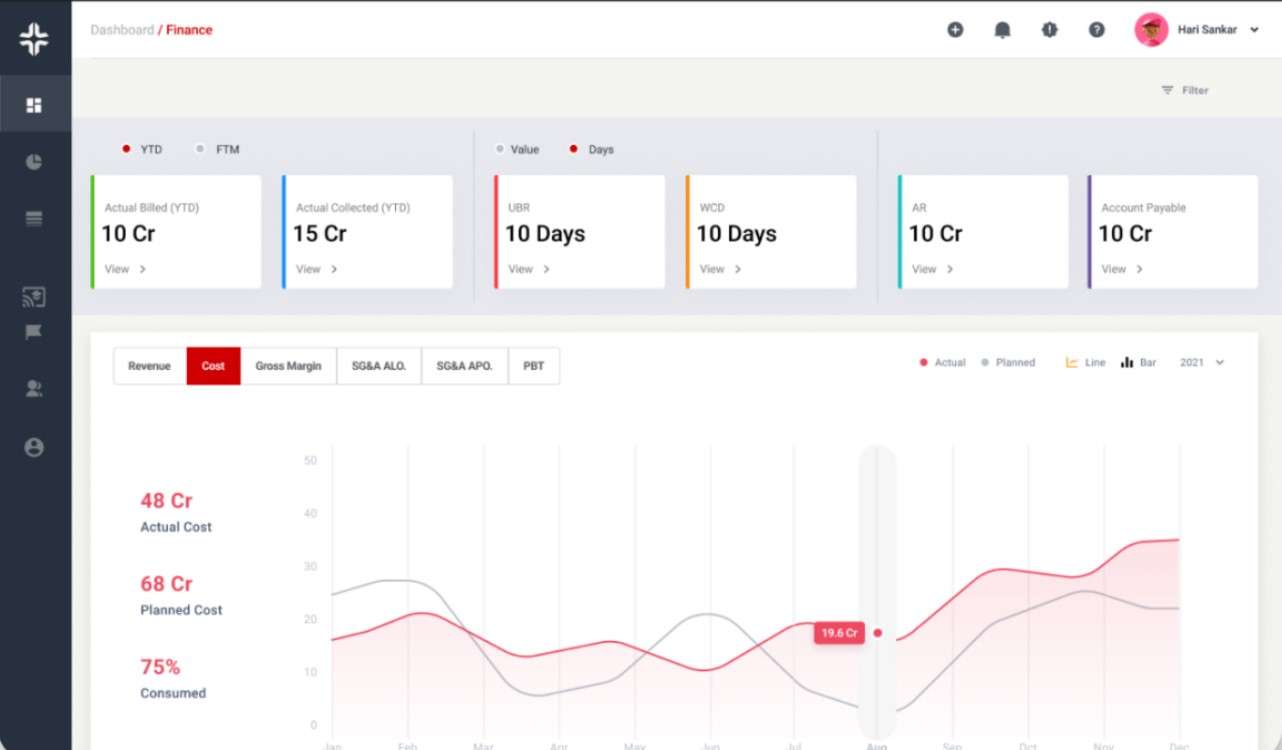
KEBS Finance Management
Ready to optimize your AP Ratio and drive your business to new heights? Contact us today or get a firsthand experience with a demo.



