Home » PSApedia
Data retention policy compliance
Achieve Data Retention Policy Compliance - Safeguard Information and Uphold Regulations.
What is Data Retention Policy Compliance?
Data retention policy compliance refers to the adherence to established guidelines and regulations regarding the storage and preservation of data for a specific period. This policy ensures that organizations retain essential data for operational, legal, or regulatory purposes while also ensuring that unnecessary data is deleted in a timely and secure manner.
In the context of Professional Service Automation (PSA), data retention becomes crucial. PSA tools, like KEBS, handle vast amounts of sensitive client and project data. Ensuring this data is retained and deleted as per compliance standards is vital for both operational efficiency and legal protection.
Importance of Data Retention Policy Compliance
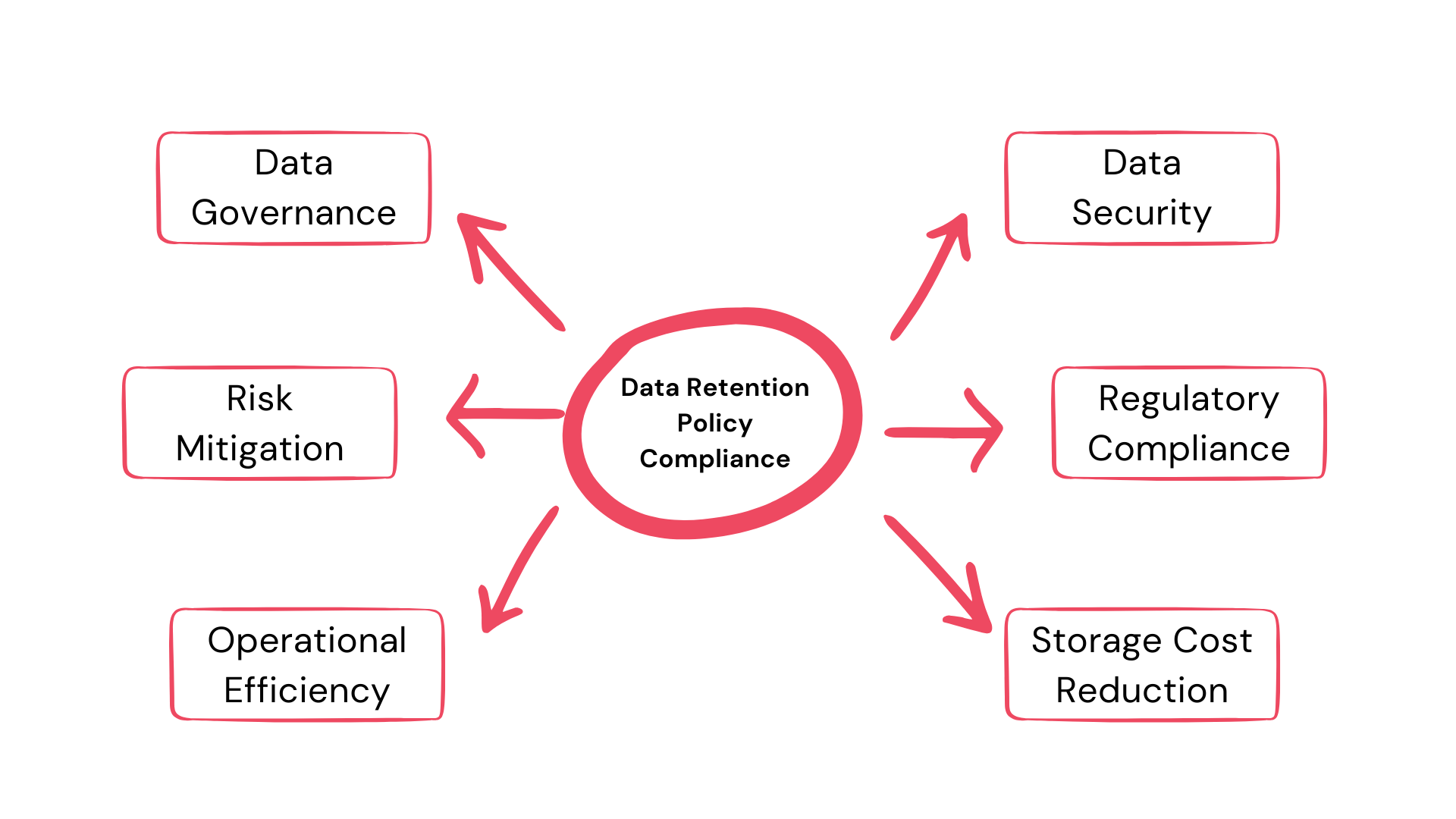
Data retention policy compliance is not just a matter of following rules; it’s about safeguarding an organization’s reputation, ensuring operational efficiency, and avoiding legal pitfalls. Here’s why it’s essential:
1. Legal and Regulatory Adherence: Many industries have specific regulations regarding how long certain types of data must be retained. Non-compliance can lead to hefty fines and legal complications.
2. Operational Efficiency: Retaining unnecessary data can clutter databases, making it harder to find relevant information. Efficient data management can streamline operations.
3. Protecting Stakeholder Interests: Clients, employees, and other stakeholders trust organizations with their data. Proper data retention ensures this trust isn’t misplaced.
4. Cost Management: Storing data isn’t free. By ensuring only necessary data is retained, organizations can save on storage costs.
Importance of Data Retention Policy Compliance
How to Calculate Data Retention Period?
Calculating the appropriate data retention period is crucial for compliance. While the exact duration might vary based on industry regulations and company policies, a general formula can be:
Data Retention Period = (Duration of Project or Client Engagement + Legal Requirement Duration) – Time Since Last Access
Example:
Let’s say a PSA tool is used for a project that lasted 2 years. The industry regulation mandates that data related to such projects be retained for 5 years. If the data was last accessed 1 year ago, the retention period would be:
= (2 years + 5 years) – 1 year
= 6 years
Thus, the data should be retained for 6 more years before considering deletion.
Difference Between Data Retention and Data Backup
While both data retention and data backup involve storing data, they serve different purposes:
1. Data Retention: This refers to the deliberate storage of data for compliance with legal or operational requirements. The focus is on preserving specific data for a set period.
2. Data Backup: This is about creating copies of data to prevent data loss in case of system failures, errors, or other unforeseen issues. It’s more about data recovery than compliance.
For instance, while using a project management tool, data retention would ensure that project details are stored for a specified period post-completion. In contrast, data backup would ensure that ongoing project data is regularly copied to prevent any loss.
| Aspect | Data Retention | Data Backup |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Preserve data for compliance and historical purposes. | Create copies of data to recover from loss or corruption. |
| Data Lifecycle | Focuses on long-term storage of data, typically for legal or regulatory requirements. | Focuses on periodic copies of current data for recovery in case of data loss or system failures. |
| Accessibility | Data retained is often less accessible and may require specific access procedures or policies. | Data backups are readily accessible for quick recovery. |
| Data Versions | Retained data may not have multiple versions and may be immutable. | Backups often include multiple versions of data to recover from different points in time. |
How Data Retention Policy Compliance is Used?
Data retention policy compliance is used in various ways:
1. Audit Trails: Organizations can provide a clear trail of historical data for auditing purposes, ensuring transparency and trustworthiness.
2. Legal Protection: In case of legal disputes, retained data can serve as evidence, protecting the organization’s interests.
3. Operational Reference: Past data can be referred to for insights, helping in decision-making and strategy formulation.
For instance, in the realm of financial management, retaining transaction records can help in reconciliations, audits, and financial planning.
Ready to Optimize Your Data Retention Policy Compliance?
KEBS, as a leading PSA software, offers robust features to ensure data retention policy compliance. With KEBS, organizations can generate detailed reports showcasing their adherence to data retention policies, useful for audits and stakeholder communication.
KEBS ensures that retained data is stored securely, preventing unauthorized access and breaches.
KEBS Project Management
Ready to optimize your data retention policy compliance? Contact KEBS or request a demo to see how KEBS can streamline your data management processes.



