What is Dividend Yield?
Dividend Yield is a financial ratio that measures the amount of cash dividends paid out to shareholders relative to the market value of a company’s shares.
It’s an indicator of the return on investment a shareholder gets from dividends alone, excluding any capital gains. In Professional Service Automation (PSA), understanding this metric is essential for financial planning and investment strategies.
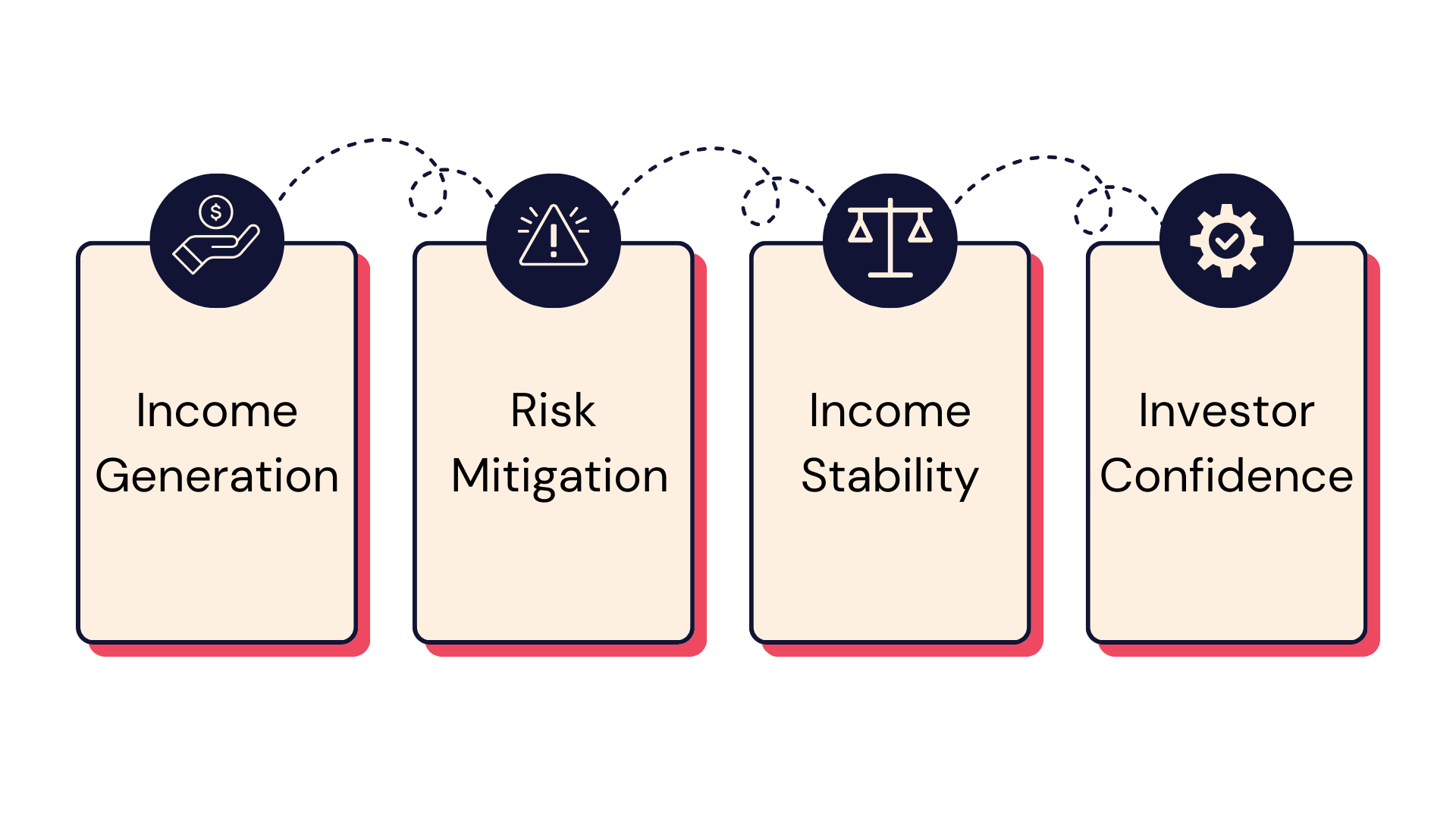
The Importance of Dividend Yield
Understanding Dividend Yield holds significant importance for both individual investors and institutions. For investors seeking stable income streams, a high Dividend Yield indicates a potential for regular and substantial returns. It’s also indicative of a company’s financial stability and consistent performance.
1. Investment Attractiveness: A higher dividend yield can make a stock more attractive to investors seeking regular income.
2. Company Health Indicator: Consistent dividend payments often reflect the company’s stable earnings and financial health.
3. Portfolio Strategy: For investors focusing on income, especially in the PSA sector, dividend yield is a crucial component in portfolio building.
The Importance of Dividend Yield
How to calculate Dividend Yield?
Formula:
Dividend Yield = (Annual Dividends per Share/Price per Share) × 100
Example:
If a company pays an annual dividend of $2 per share and its current stock price is $40, the dividend yield would be:
Yield = (2/40) × 100 = 5%
Dividend Yield vs Other Financial Metrics
Comparing Dividend Yield with related financial metrics like Earnings per Share (EPS) or Price to Earnings (P/E) ratio is crucial. While EPS reflects a company’s profitability, Dividend Yield specifically assesses returns through dividends. P/E ratio, on the other hand, compares a company’s stock price to its earnings per share.
1. Earnings Per Share (EPS): EPS measures the profitability of a company; dividend yield, on the other hand, shows the return on investment through dividends.
2. Price-to-Earnings (P/E) Ratio: While the P/E ratio evaluates the value of a company’s shares relative to its earnings, dividend yield is focused on the return from dividends.
3. Total Return: Total return accounts for both capital gains and dividends, whereas dividend yield exclusively measures the income from dividends.
| Aspect | Dividend Yield | Earnings Per Share (EPS) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A financial ratio that shows how much a company pays out in dividends relative to its share price | Net earnings divided by the total number of outstanding shares |
| Use / Purpose | Indicates the return on investment from dividends for shareholders | Measures a company’s profitability and the amount of earnings available to shareholders |
| Calculation | (Dividends per Share / Current Market Price per Share) x 100 | Net Earnings / Number of Outstanding Shares |
Application of Dividend Yield
It aids investors in making informed decisions about their investment portfolios. It serves as a barometer for selecting income-generating stocks and balancing investment strategies between growth and income.
1. Income Generation: High-dividend-yield stocks can provide a steady income stream, which is crucial for investors relying on investments for income.
2. Risk Assessment: Dividend yield can indicate the risk level; extremely high yields might be unsustainable.
3. Sector Analysis: Different sectors have varying typical dividend yields; understanding these can guide investment choices in the PSA sector.
Ready to Optimize Your Dividend Yield?
Utilizing KEBS financial management tools, investors and companies in the PSA sector can optimize their dividend strategies. KEBS provides insights , aiding in informed investment decisions.
The risk management tools in KEBS help assess the sustainability of dividends.
KEBS Finance Management
Considering enhancing your investment strategy or financial planning in the PSA sector? Contact KEBS for advanced solutions or request a demo to see how our software can help in maximizing your financial performance.



