What Is EBITDA Rate?
EBITDA Rate is an important finance metric that shows how profitable a company is without considering interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization. This rate only considers operational success and does not include financing structures, tax rates, or non-cash expenses.
The EBITDA rate in financial analysis helps investors and analysts focus on a company’s earnings from its main business activities. It does not take into account the impact of financing choices, taxes, and non-cash accounting changes. By looking at this measure, stakeholders can see how well a company can make money from its main business activities.
Why EBITDA Rate Is So Important?
EBITDA, which stands for Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortization, is a widely used financial metric that provides a snapshot of a company’s operating performance. The EBITDA rate is important because it strips away the effects of financing decisions, tax environments, and non-cash expenses, allowing for a clearer comparison of operational profitability between companies and across industries.
This makes it a crucial tool for investment decisions, valuation purposes, and strategic planning. EBITDA Rate provides an undiluted view of a company’s operational performance. Here’s why it holds paramount importance:
- Comparative Analysis: EBITDA Rate allows analysts to compare companies across industries without the influence of financing and accounting decisions.
- Investor Attraction: Higher EBITDA can make a company attractive to investors, as it can indicate good cash flow.
- Financial Flexibility: Companies with a high EBITDA Rate might have more resources to invest in growth opportunities or reduce debt.

Why EBITDA Rate Is So Important?
How to Calculate EBITDA Rate?
Formula: EBITDA = Net Income + Interest + Taxes + Depreciation + Amortization
Example: Let’s assume Company X reports the following for a fiscal year:
- Net Income: $1,000,000
- Interest: $50,000
- Taxes: $150,000
- Depreciation: $100,000
- Amortization: $50,000
Using the formula: EBITDA = $1,000,000 + $50,000 + $150,000 + $100,000 + $50,000 = $1,350,000
Hence, Company X has an EBITDA of $1,350,000.
EBITDA Rate vs. Net Profit vs. Operating Profit
EBITDA, Net Profit, and Operating Profit are three key financial metrics used to gauge the profitability and operational efficiency of a company. EBITDA (Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortization) focuses on the operating performance by analyzing earnings from core business operations without considering interest, tax, and non-cash expenses.
EBITDA Rate: As discussed, this is the company’s profitability without considering interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization.
Net Profit: This is the actual profit after all deductions including taxes and interest are made. A detailed analysis on improving net profit can be found here.
Operating Profit: It’s the profit after the deduction of operating expenses like wages and rent but before interest and taxes. For strategies to optimize operating profit, this article can be helpful.
| Metric | Definition | Formula |
|---|---|---|
| EBITDA (Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortization) | Profit of a company before accounting for interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization. | Revenue – Operating Expenses ± Other Income (excluding interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization) |
| Operating Profit (or EBIT – Earnings Before Interest and Taxes) | Profit generated from core operations before accounting for interest and taxes. | Revenue – Operating Expenses ± Other Income (excluding interest and taxes) |
| Net Profit (or Net Income) | The actual profit left after all expenses, including interest and taxes, have been deducted. | Revenue – Total Expenses |
How EBITDA Rate Is Used in Financial Analysis?
EBITDA is particularly useful for comparing companies within the same industry, as it removes extraneous factors and provides a more apples-to-apples comparison of operational strength. EBITDA is important, but it doesn’t include capital expenses or changes in working capital. So, you should look at it with other financial measures for a complete analysis. Financial analysts leverage EBITDA Rate in various ways:
- Valuation: It can be used to calculate the enterprise value of a firm.
- Investment Decisions: Investors might look for companies with rising EBITDA margins, which could indicate improving operational efficiency.
- Loan Covenants: Lenders might set covenants based on EBITDA, given it reflects the ability to generate cash.
To enhance financial analysis further, using advanced financial management software can be beneficial.
Ready to Optimize Your EBITDA Rate?
Understanding your EBITDA Rate is just the start. To optimize and make actionable decisions, you need robust tools and solutions. KEBS, a renowned PSA Software, provides comprehensive financial analytics and insights that empower businesses to improve their operational profitability.
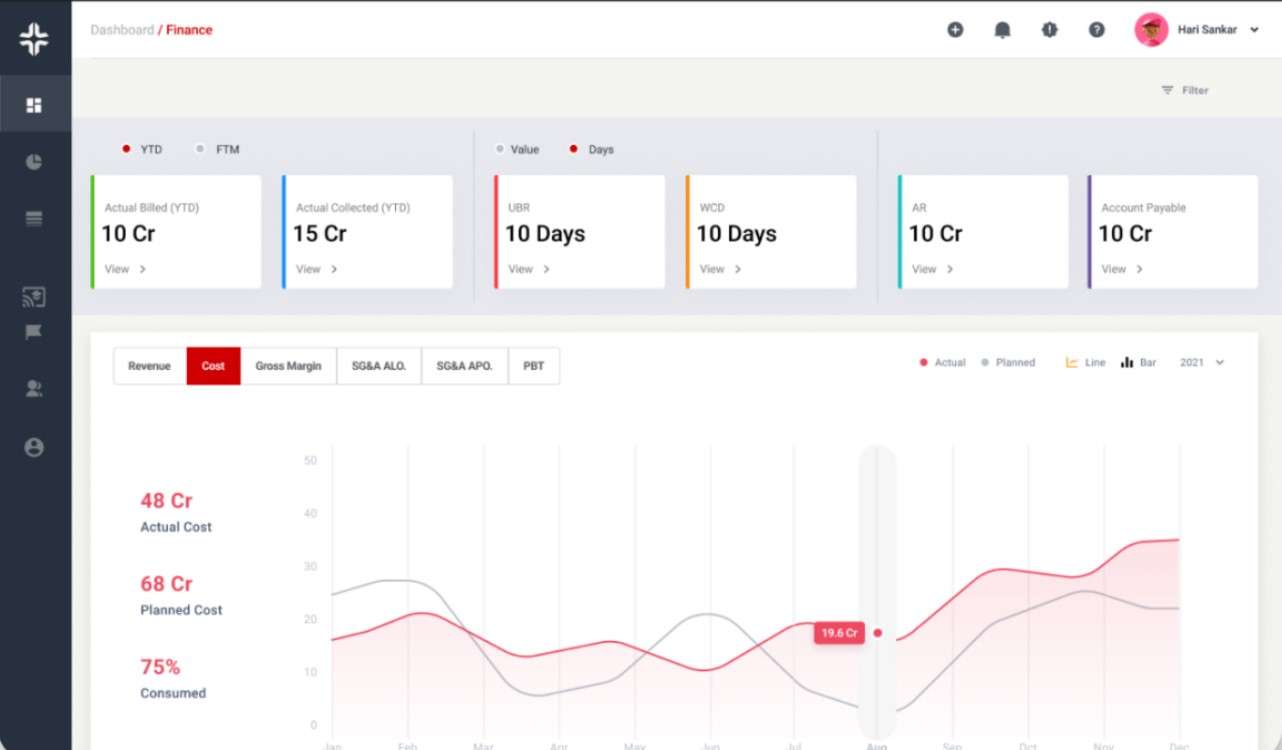
KEBS Finance Management
Explore more on how KEBS can elevate your financial management by booking a demo or contacting our team today!



