Home » PSApedia
Net Interest Margin
Discover Insights on Net Interest Margin. Fine-Tune Strategies and Maximize Profitability.
What is Net Interest Margin (NIM)?
Net Interest Margin (NIM) is a crucial metric in the world of Professional Services and banking. It measures the difference between the interest income generated by banks or other financial institutions and the amount of interest paid out to their lenders (for example, on deposits), relative to the amount of their interest-earning assets.
Essentially, NIM helps in understanding how successful a financial institution is in its core business activities: lending and borrowing.
The Significance of NIM in Financial Management
NIM is a key indicator of a bank’s profitability and financial health. A higher NIM suggests that the institution is managing its investment and lending strategies effectively, yielding more income from its interest-earning assets than it pays on its liabilities.
It’s particularly important in the context of financial management software, where monitoring profitability and operational efficiency is crucial.
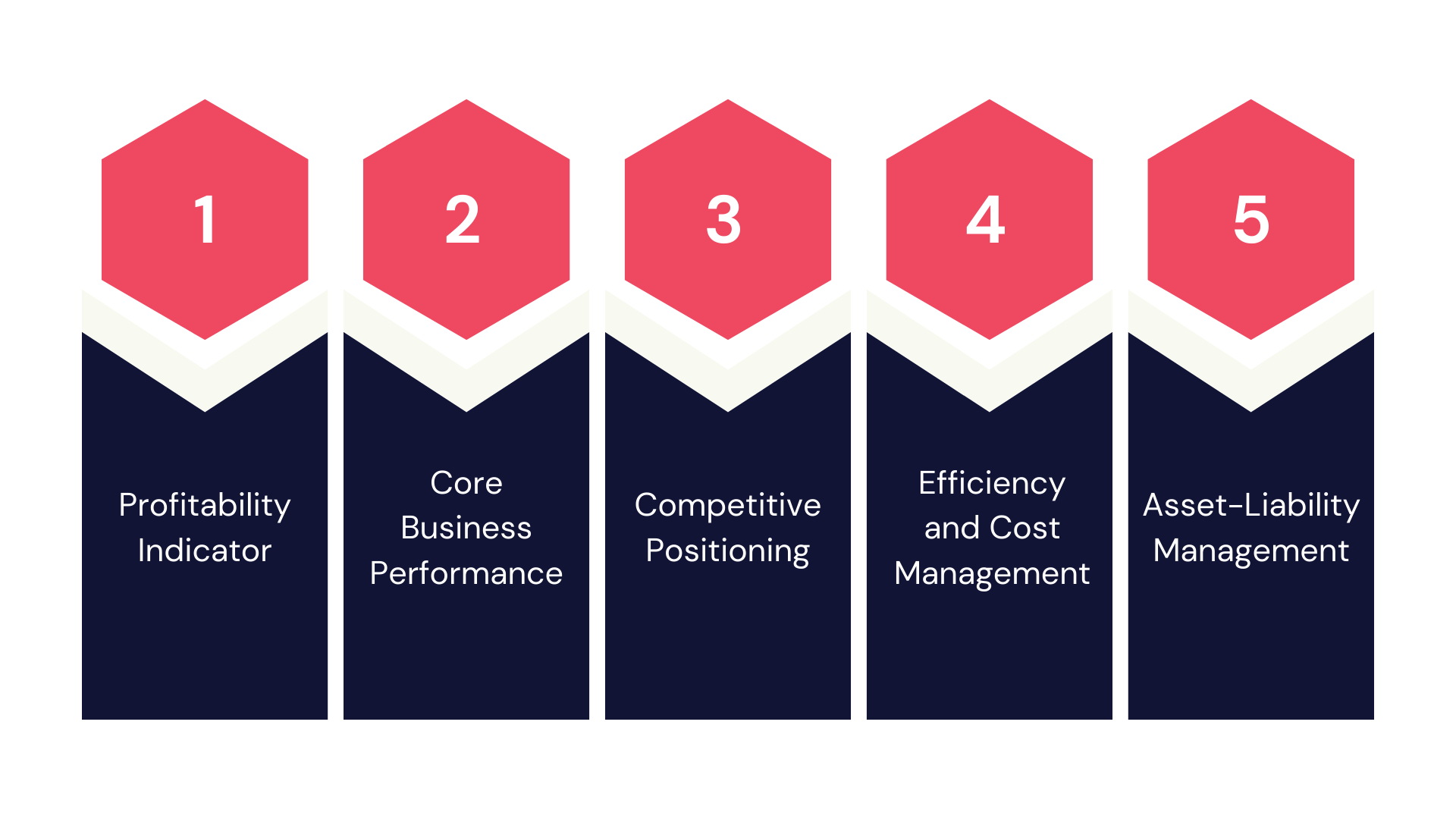
Significance of Net Interest Margin
How to calculate Net Interest Margin?
The formula for calculating NIM is:
NIM = Interest Income − Interest Expense / Average Earning Assets
For example, if a bank earns $20 million in interest from loans and pays $10 million in interest on deposits, and its average earning assets are $200 million, its NIM would be:
- Interest Income = $20 million
- Interest Expenses = $10 million
- Average Earning Assets = $200 million
NIM = (Interest Income – Interest Expenses) / Average Earning Assets
NIM = ($20 million – $10 million) / $200 million
NIM = $10 million / $200 million
NIM = 0.05 or 5%
This means the bank is earning a net interest margin of 5% on its assets.
Net Interest Margin vs Other Financial Ratios
While NIM focuses on the profitability of a bank’s lending and borrowing activities, it’s different from other financial ratios like the Return on Assets (ROA) or Return on Equity (ROE). ROA measures overall profitability relative to total assets, while ROE assesses profitability relative to shareholders’ equity. Understanding these differences is crucial for comprehensive financial analysis.
| Ratio | Definition | Use / Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Net Interest Margin (NIM) | Difference between interest income and interest expense, divided by average interest-earning assets | Measures the profitability of a financial institution’s lending operations |
| Return on Assets (ROA) | Ratio of net income to total assets | Measures profitability relative to the total assets held |
| Return on Equity (ROE) | Ratio of net income to shareholders’ equity | Indicates the profitability of a company in relation to shareholders’ investments |
| Efficiency Ratio | Ratio of operating expenses to revenue | Measures the efficiency of an institution in managing its expenses |
Strategies to Optimize Net Interest Margin
Optimizing NIM involves strategies like diversifying loan portfolios, managing interest rate risks, and improving the cost efficiency of operations.
Financial institutions can use tools like financial management to analyze interest income and expenses, manage risks, and make informed decisions to improve their NIM.
Ready to Optimize Your NIM?
KEBS offers advanced financial management software that can significantly enhance the management of NIM. KEBS provides tools for analyzing interest income and expenses, helping in more accurate NIM calculations.
Through KEBS risk management features, financial institutions can better understand and manage the risks associated with their interest-earning assets. With KEBS, institutions can access comprehensive market insights and trend analyses, essential for strategic planning and maintaining a healthy NIM.
Streamlining financial operations reduces costs, indirectly contributing to a better NIM.
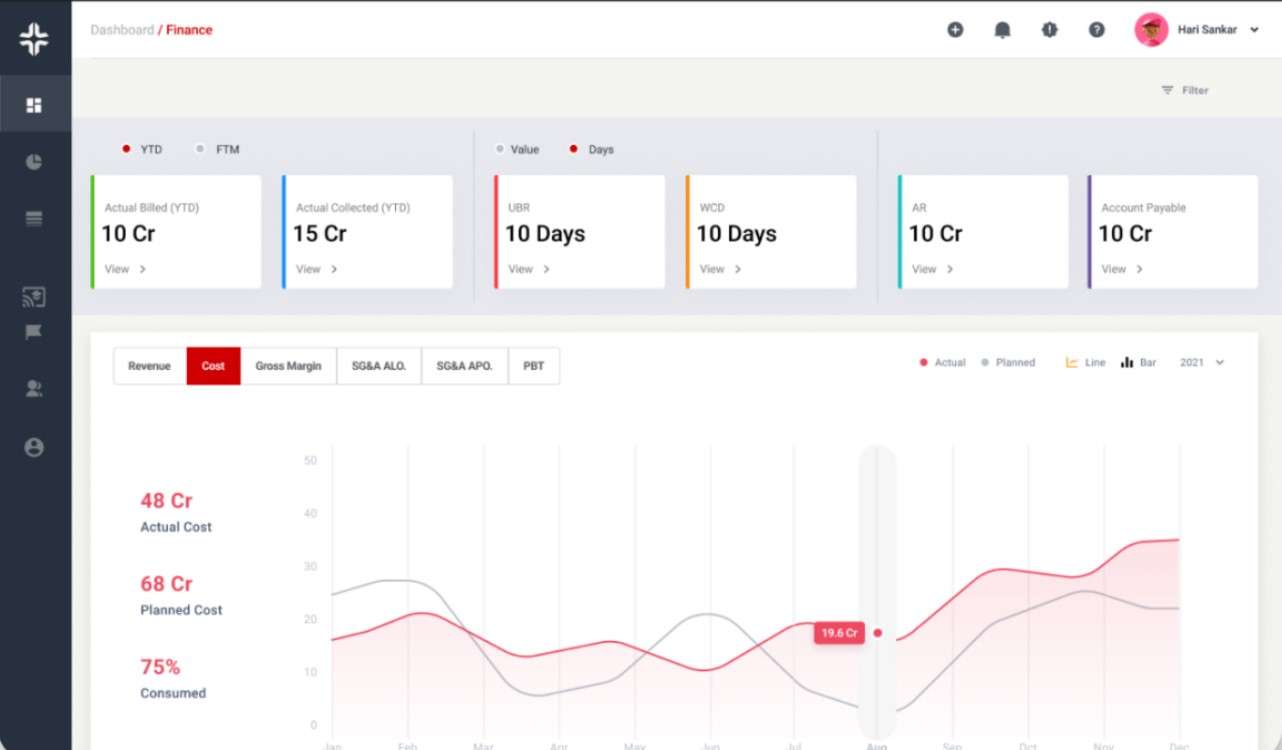
KEBS Finance Management
To discover more about how KEBS can assist in optimizing your financial institution’s Net Interest Margin, contact us for further information or request a demo to see our financial tools in action.



