Home » PSApedia
Profit margin
Enhance Profitability with Strategic Insights on Profit Margin. Optimize Revenue and Maximize Success.
What is Profit Margin?
Profit margin is a financial metric that represents the percentage of profit a company earns relative to its revenue.
It’s a measure of a company’s profitability and is used to assess how well a company can turn revenues into profit after deducting all expenses.
Importance of Profit Margin
Understanding profit margin is crucial for businesses as it provides insights into operational efficiency. A higher profit margin indicates a more profitable company that has better control over its costs compared to its competitors.
1. Operational Efficiency: A higher profit margin can indicate efficient operations and effective cost management.
2. Investor Attraction: Investors often look at profit margins to determine the health of a business. A consistent profit margin can attract more investors.
3. Pricing Strategy: Profit margin can guide businesses in setting the right pricing strategy. By understanding how different pricing can impact profit margins, businesses can make informed decisions.
4. Financial Stability: Companies with higher profit margins can weather economic downturns better than those with thin margins.

Importance of Profit Margin
Calculating Profit Margin
Formula:
Profit Margin = (Net Profit/Revenue) × 100
Example:
Let’s say a company has a net profit of $50,000 and revenue of $200,000.
Profit Margin=(50,000/200,000)×100=25%
This means that for every dollar the company earns, it keeps $0.25 as profit.
Profit Margin vs Other Financial Metrics
Understanding the differences between these metrics can help businesses get a clearer picture of where their money is going and where efficiencies can be gained. Profit margin is often compared to other financial metrics to get a comprehensive view of a company’s financial health:
1. Gross Margin: Represents the percentage of revenue that exceeds the cost of goods sold. It doesn’t account for other expenses like profit margin does.
2. Operating Margin: Focuses on operating income, which is the profit after deducting operating expenses but before interest and taxes.
3. Net Margin: This is essentially the profit margin, representing net profit as a percentage of revenue.
| Metric | Description | Key Differences from Profit Margin |
|---|---|---|
| Profit Margin | Measures profitability by comparing net income to revenue. Typically expressed as a percentage. | Focuses solely on profitability and may not account for operational efficiency or productivity. |
| Gross Margin | Measures the profitability of goods or services before operating expenses are considered. | Excludes operating expenses, giving an idea of the core profitability of the services provided. |
| Earnings Before Interest and Taxes (EBIT) | Focuses on operating profitability by excluding interest and taxes. | Ignores financial leverage and tax implications, providing a clearer view of operational performance. |
| Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) | Estimates the long-term value of a customer relationship, including repeat business and referrals. | Focuses on customer relationships and loyalty rather than direct financial performance. |
How Profit Margin is Used in Business?
Profit margin serves various purposes in business:
1. Performance Evaluation: Companies often use profit margin to evaluate their performance over time or compare it against competitors.
2. Strategic Planning: By understanding profit margins, companies can set realistic goals and create strategies to achieve them.
3. Resource Allocation: Companies can decide where to allocate resources more effectively by understanding which products or services have higher profit margins.
4. Financial Forecasting: Profit margins can help in predicting future profitability and cash flows.
Ready to Optimize Your Profit Margin?
KEBS, a leading Professional Service Automation (PSA) software, offers tools that can help businesses optimize their profit margins. With KEBS finance management software, businesses can keep track of their revenues and expenses, helping them understand and improve their profit margins.
Efficient resource allocation can lead to cost savings. KEBS resource management software ensures that businesses utilize their resources optimally. Proper project management can prevent cost overruns. KEBS project management tools, including the Gantt chart, help businesses keep their projects on track and within budget. KEBS deal management software ensures that businesses can track and manage their deals effectively, leading to increased revenues.
Efficient ticket resolution can lead to increased customer satisfaction and repeat business. KEBS ticket management software ensures that customer issues are resolved promptly. By integrating these tools, businesses can effectively manage their operations, leading to improved profit margins.
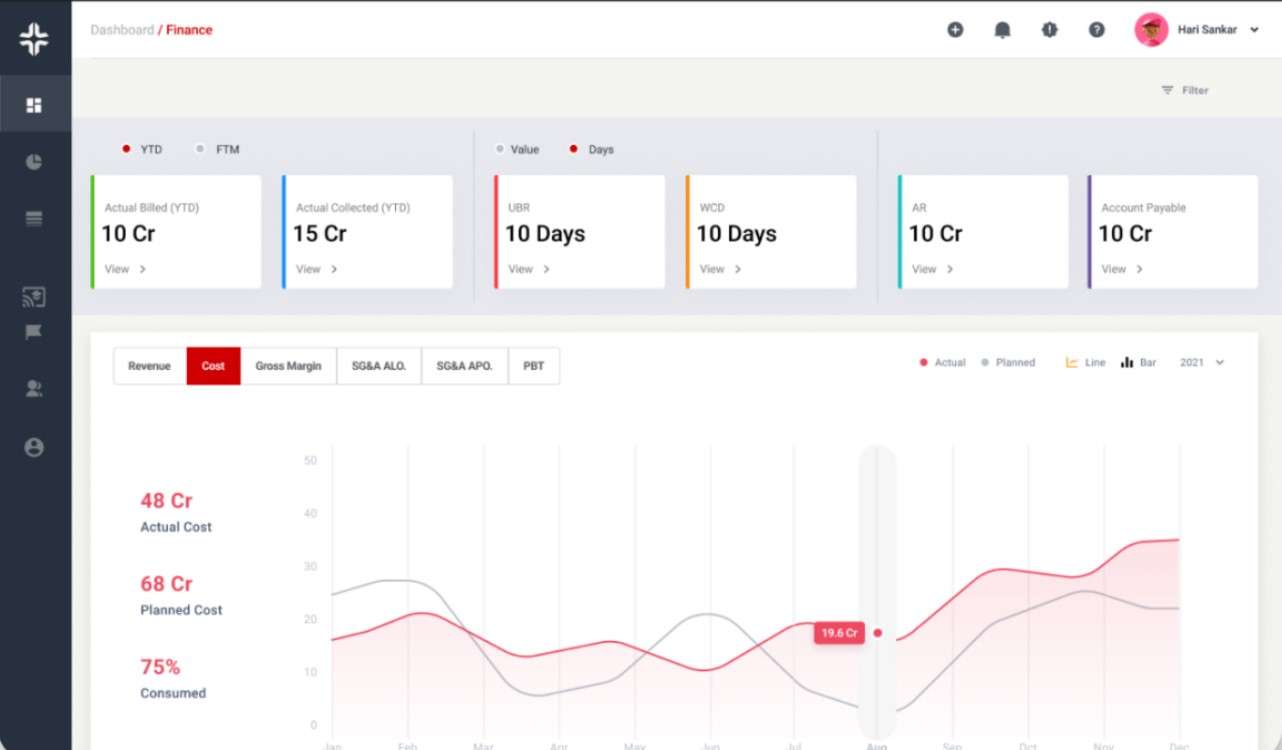
KEBS Finance Management
Ready to Optimize Your Profit Margin with KEBS? Contact us today or request a demo to see how KEBS can transform your business operations.



