Home » PSApedia
Resource Attrition Rate
Gauge Efficiency with Resource Attrition Rate Analysis. Enhance Productivity and Minimize Losses.
What is Resource Attrition Rate?
Resource Attrition Rate refers to the percentage of employees or resources that leave an organization during a specified period. In the context of Professional Service Automation (PSA), it measures the turnover of resources involved in service delivery, project management, and other related tasks.
Resource Attrition Rate, within the context of Professional Service Automation (PSA), refers to the percentage of employees who leave the organization over a specified period. This metric is crucial for service-oriented firms, as it impacts the organization’s capacity to deliver projects effectively.
Importance of Resource Attrition Rate
The Resource Attrition Rate, often just referred to as attrition rate, is a crucial metric for organizations as it reflects the rate at which employees leave the company over a certain period. Monitoring this rate is essential for understanding the organization’s stability and the effectiveness of its retention strategies. Understanding the Resource Attrition Rate is crucial for several reasons:
1. Operational Efficiency: High attrition can disrupt ongoing projects and lead to inefficiencies.
2. Financial Impact: Recruiting and training new resources can be costly.
3. Client Relationships: Frequent changes in project teams can affect client trust and satisfaction.
4. Resource Management: Attrition insights can help in better resource allocation and forecasting.

Importance of Resource Attrition Rate
Calculating Resource Attrition Rate
Formula:
Resource Attrition Rate = (Number of Resources that Left / Total Number of Resources at Start of Period) × 100
Example:
If a PSA firm starts the year with 100 resources and 10 leave during the year, the Resource Attrition Rate is:
Attrition Rate=(10/100)×100=10%
Resource Attrition Rate vs Other Metrics
1. Resource Utilization Rate: While attrition measures resource turnover, utilization rate measures how effectively resources are being used.
2. Resource Allocation Rate: This metric indicates how resources are distributed across projects, whereas attrition focuses on resource departure.
3. Employee Satisfaction Rate: While both metrics can provide insights into resource contentment, satisfaction rate directly gauges resource happiness and engagement.
| Metric | Definition | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Resource Attrition Rate | Rate at which employees leave the organization | Indicates stability, impacts costs, and talent retention |
| Utilization Rate | Hours billed vs. hours worked | Measures efficiency and profitability of resource allocation |
| Project Margin | Revenue minus project costs | Indicates profitability and financial health of projects |
| Customer Satisfaction | Measured through feedback and surveys | Reflects quality of service and impacts client retention |
Application of Resource Attrition Rate in PSA
In PSA, the Resource Attrition Rate can be used to:
1. Forecasting: Predict future resource requirements and plan for recruitment.
2. Performance Analysis: Identify departments or projects with high attrition and investigate underlying issues.
3. Strategic Planning: Align HR strategies with business goals to reduce attrition.
4. Client Communication: Inform clients about resource stability in their projects, enhancing trust.
Effective resource management in PSA can significantly reduce attrition by ensuring that resources are well-utilized, satisfied, and aligned with projects that match their skills and interests.
Ready to Optimize Your Resource Attrition Rate?
KEBS, a leading PSA software, offers tools to manage and reduce Resource Attrition Rate. Provides a holistic view of each resource, helping managers understand resource needs and challenges. Discover the potential of KEBS Employee 360.
From Gantt charts to resource allocation, KEBS ensures projects are well-managed, reducing resource dissatisfaction.
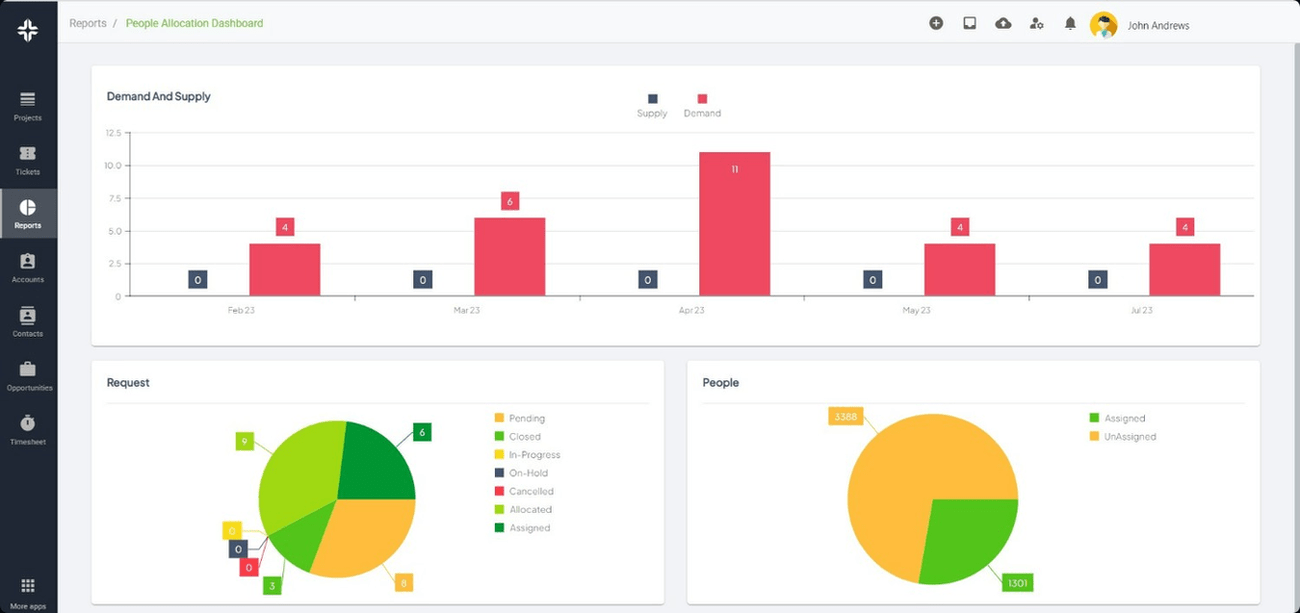
KEBS Resource Management
Ready to optimize your Resource Attrition Rate? Contact KEBS or request a demo to see how KEBS can transform your PSA operations.



