Home » PSApedia
Return on Equity
Explore Return on Equity (ROE) Metrics. Evaluate Financial Performance, Optimize Investments.
What is Return on Equity (ROE)?
ROE is a measure of how profitable a company is for its shareholders. It shows how well the company uses its equity. ROE measures how effectively a company is making money from the money invested by shareholders, including retained earnings and capital.
A higher ROE indicates that the company is effectively utilizing its equity to generate profits. On the other hand, a lower ROE suggests the opposite. Investors and analysts use this metric to compare a company’s profitability and financial performance with similar companies.
Importance of ROE
By comparing ROE across firms in the same sector, investors can discern which companies are better at converting equity investments into profits. Moreover, tracking ROE over time can provide insights into managerial efficiency and the potential sustainability of a firm’s profitability. ROE is a pivotal tool in the world of finance for various reasons:
1. Profitability Indicator: ROE indicates how profitably a company is using shareholders funds.
3. Investment Decisions: High ROE values might suggest that a company is adept at generating profit without necessitating excessive capital.
Why Return on Equity is so important?
How to Calculate ROE?
ROE is computed using the formula:
ROE = Net Income / Shareholder’s Equity
Example:
Let’s consider a company, XYZ Corp. If XYZ Corp reported a net income of $5 million and its shareholder’s equity amounted to $25 million, then:
ROE=5/25=0.20
Thus, the ROE for XYZ Corp is 20%, indicating it generated a 20% return on the shareholders’ equity.
Difference Between ROE and Related Metrics
Understanding these differences aids businesses in comprehensive financial management. ROE, while crucial, is not the only performance metric. For instance:
1. ROE vs Return on Assets (ROA): ROA relates net income to total assets, determining how efficiently a company’s assets generate profit. ROE, however, ties net income to shareholder equity.
2. ROE vs Return on Invested Capital (ROIC): ROIC measures returns on all capital invested, including debt. It’s broader than ROE which only considers equity.
| Metric | Definition | Formula |
|---|---|---|
| ROE (Return on Equity) | Net Income divided by Shareholder’s Equity | ROE = Net Income / Shareholder’s Equity |
| ROA (Return on Assets) | Net Income divided by Total Assets | ROA = Net Income / Total Assets |
| ROCE (Return on Capital Employed) | Net Income divided by Capital Employed (Debt + Equity) | ROCE = Net Income / (Debt + Equity) |
| ROI (Return on Investment) | Gain from Investment minus Cost of Investment divided by Cost of Investment | ROI = (Gain from Investment – Cost of Investment) / Cost of Investment |
Usage of ROE
ROE’s primary utility is in:
1. Performance Assessment: Companies routinely track ROE to ensure they’re using shareholders equity efficiently.
2. Strategic Planning: Firms use ROE to set performance benchmarks and make informed project management decisions.
3. Investment Decisions: Investors and analysts employ ROE for identifying promising investment opportunities by comparing companies.
Ready to Optimize Your ROE?
KEBS, being a leading Professional Service Automation (PSA) software, can be pivotal for businesses striving to optimize their ROE. Here’s how:
- Enhanced Financial Management: With KEBS finance management software, businesses can effortlessly track financial metrics, including ROE, ensuring sound decision-making.
- Resource Optimization: Efficient resource management ensures that shareholder funds are employed effectively, which can subsequently bolster ROE.
- Strategic Decision Support: Utilizing KEBS’s project management tools, like Gantt charts, companies can drive projects to fruition effectively, positively influencing ROE.
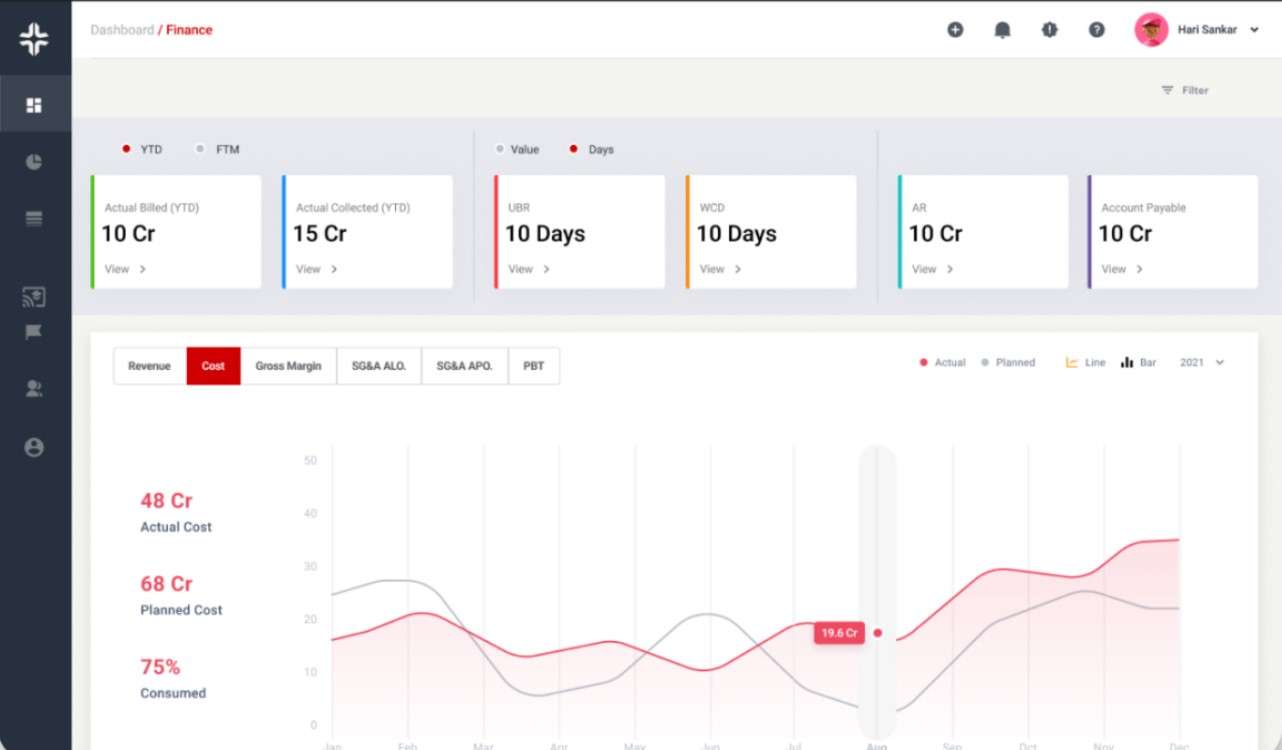
KEBS Finance Management
To delve deeper into how KEBS can refine your ROE metrics and other financial goals, contact us or explore a comprehensive demo.



