Home » PSApedia
Break-Even Point
Calculate Your Break-Even Point with Precision. Make Informed Decisions and Achieve Profitability.
What is the Break-Even Point?
The Break-Even Point (BEP) is a fundamental financial concept that denotes the point where total costs (both fixed and variable) equal total revenue. In simpler terms, it’s the point where a business neither makes a profit nor incurs a loss.
Understanding the BEP is crucial for businesses, especially in the realm of Professional Service Automation (PSA), where efficient resource allocation and financial management are paramount.
Importance of the Break-Even Point
In the context of PSA, the BEP is not just a theoretical concept but a practical tool. Here’s why:
1. Risk Assessment: Knowing the BEP helps businesses assess the risk associated with their operations. If a company operates below its BEP, it’s incurring losses.
2. Pricing Strategy: BEP aids in setting the right price for services. By understanding the costs involved, businesses can price their services to ensure profitability.
3. Financial Planning: BEP is a cornerstone for financial management in PSA, helping businesses plan their budgets and forecast future financial needs.
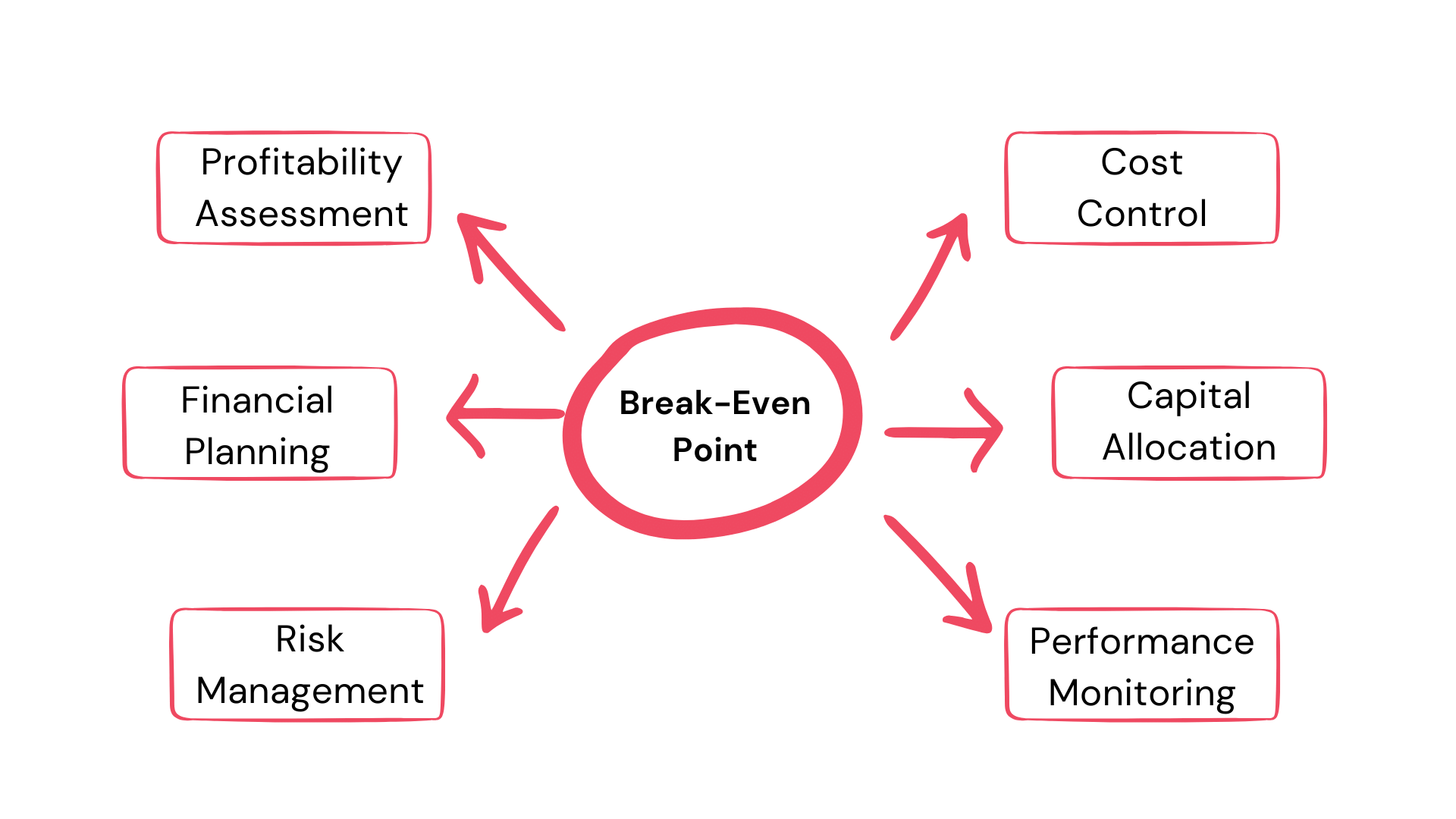
Why Break-Even Point is so important?
Calculating the Break-Even Point
Formula:
Break-Even Point (in units) = Fixed Costs/Selling Price per Unit − Variable Cost per Unit
Example:
Imagine a PSA company that offers consulting services. Their fixed costs (like salaries, rent, and utilities) amount to $100,000 annually. They charge clients $200 per consulting hour, and the variable costs (like travel and materials) per hour are $50.
Using the formula:
BEP=100,000/200−50
BEP=100,000/150
BEP=666.67
This means the company needs to bill 667 consulting hours to break even.
Break-Even Point vs Other Financial Metrics
While the BEP is a pivotal metric, it’s essential to differentiate it from other financial metrics:
1. BEP vs Gross Profit: Gross profit is the total revenue minus the cost of goods sold (COGS). While BEP focuses on covering all costs (fixed and variable), gross profit only considers variable costs.
2. BEP vs Net Profit: Net profit is what remains after all expenses (including operational and non-operational) are deducted from the revenue. A company can have a positive net profit but still operate below its BEP.
For a deeper dive into financial metrics, consider exploring KEBS whitepaper on optimizing project financials.
| Metric | Break-Even Point (BEP) | Other Financial Metrics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The point at which total revenue equals total costs, resulting in zero profit. | Various financial metrics used to evaluate the financial health and performance of a business or project. |
| Focus | Primarily focused on identifying when an investment or project becomes financially sustainable. | Assess a broader range of financial aspects, such as profitability, liquidity, efficiency, and solvency. |
| Applicability | Typically used to evaluate the financial viability of a specific project or investment, like implementing a PSA system. | Used to assess overall company financial performance, not limited to a single project. |
| Calculation | BEP is calculated by dividing fixed costs by the contribution margin (selling price per unit minus variable cost per unit). | Various metrics include Gross Margin, Net Profit Margin, Return on Investment (ROI), and others, each with specific formulas. |
Application of the Break-Even Point in PSA
In PSA, the BEP is applied in various ways:
1. Resource Allocation: By understanding the BEP, PSA firms can allocate resources more efficiently, ensuring that projects are profitable. KEBS resource management software can be instrumental in this regard.
2. Project Evaluation: Before undertaking a project, PSA firms can use the BEP to evaluate its financial viability. This is where tools like KEBS project management software come into play.
3. Operational Efficiency: BEP can guide PSA firms in streamlining operations, from ticket management to deal management.
Ready to Optimize Your Break-Even Point?
KEBS, a leading PSA software, offers tools that can help businesses understand, calculate, and optimize their BEP. With features ranging from finance management to resource allocation, KEBS ensures that your business operates above its BEP, driving profitability.
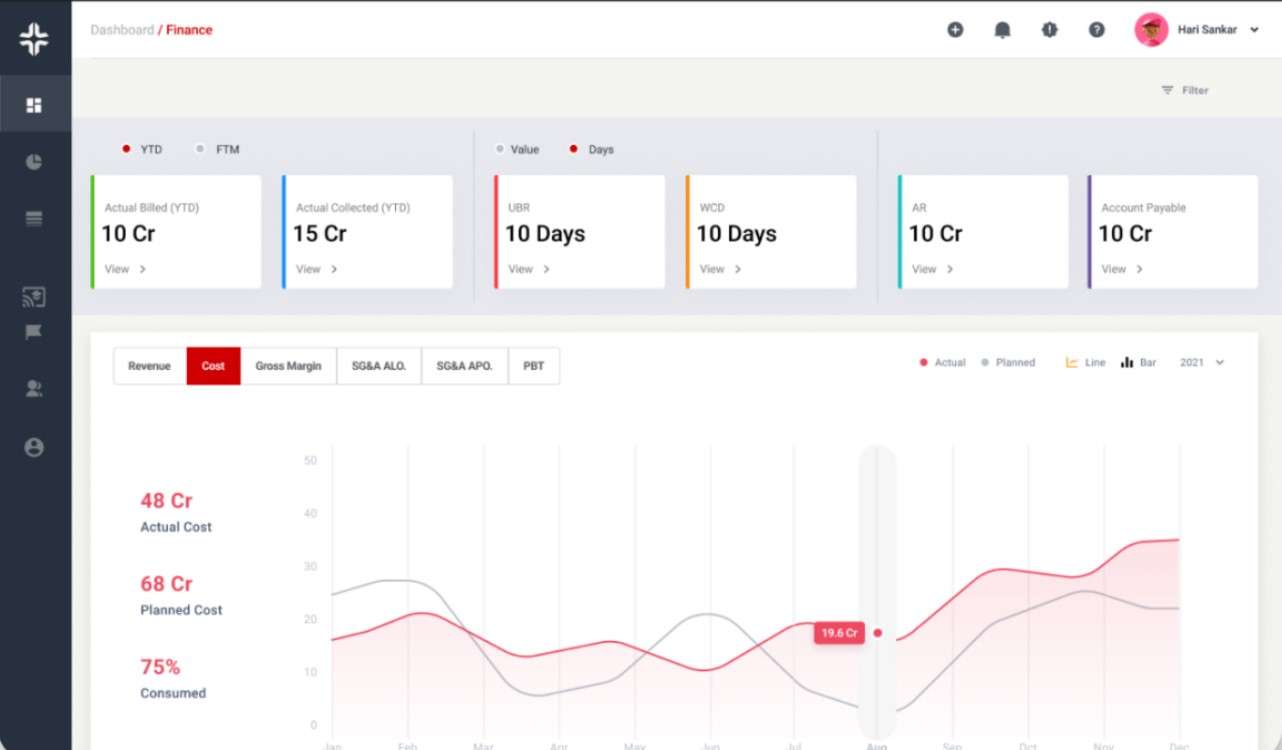
KEBS Finance Management
Ready to optimize your Break-Even Point? Contact us today or request a demo to see how KEBS can transform your PSA operations.



