Home » PSApedia
Earnings before interest and taxes
Understand Business Profitability with Earnings Before Interest and Taxes (EBIT).
Earnings Before Interest and Taxes?
Earnings Before Interest and Taxes (EBIT) is a measure of a company’s operating performance. Essentially, it represents the earnings of a business before accounting for interest and tax expenses.
It’s a tool that provides insight into the operational profitability of a company, excluding the effects of capital structure and tax strategies.
Importance of EBIT
EBIT is crucial for several reasons:
1. Operational Insight: It focuses solely on the operational aspects of a business, excluding financial and tax strategies. This makes it a pure measure of a company’s ability to generate profit from its operations.
2. Comparability: Since it excludes interest and taxes, EBIT allows for a more direct comparison between companies, especially those operating in different tax environments or with different capital structures.
3. Investment Decisions: Investors and analysts often use EBIT to assess the inherent profitability of a company, which can guide investment decisions.
For businesses, especially those using Professional Service Automation (PSA), understanding EBIT can help in making informed decisions related to operations, finance, and strategy.
Importance of EBIT
Calculating EBIT
Formula:
EBIT = Revenue−Operating Expenses
Example:
Let’s say Company A has a revenue of $1,000,000 and operating expenses (excluding interest and taxes) of $600,000.
EBIT = $1,000,000 – $600,000 = $400,000
Thus, Company A’s EBIT is $400,000.
EBIT vs Other Financial Metrics
1. EBIT vs Net Income: While EBIT focuses on operational profitability, net income considers all expenses, including interest and taxes. Net income provides a comprehensive view of a company’s overall profitability.
2. EBIT vs EBITDA: EBITDA stands for Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortization. It’s similar to EBIT but excludes depreciation and amortization expenses. EBITDA provides a view of profitability from core business operations.
3. EBIT vs Operating Profit: These terms are often used interchangeably. However, the distinction lies in the specific expenses subtracted from revenue. Operating profit might sometimes exclude other income or expenses that EBIT considers.
| Metric | Definition | Purpose/Use |
|---|---|---|
| EBIT (Earnings Before Interest and Taxes) | EBIT represents a company’s operating profit before accounting for interest expenses and taxes. | Evaluating the operational performance and profitability of a professional service organization, which may not yet account for financial leverage and tax implications. |
| EBITDA (Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortization) | EBITDA adds back depreciation and amortization expenses to EBIT. | Useful for assessing the operational cash-generating capacity of a PSA firm without the influence of non-cash expenses. |
| Net Profit | Net profit represents the earnings after accounting for all expenses, including interest and taxes. | Provides a comprehensive view of a company’s profitability after all costs and obligations are considered. |
| Gross Margin | Gross margin is the percentage difference between revenue and the cost of goods or services sold. | Indicates the efficiency of service delivery and pricing strategies. |
How EBIT is Used in Business?
For businesses operating with PSA tools like KEBS, EBIT can be seamlessly integrated into financial management strategies. EBIT is a versatile metric:
1. Performance Evaluation: Companies use EBIT to gauge their operational efficiency and profitability. It’s a key metric in performance dashboards and financial analytics.
2. Strategic Decisions: EBIT can guide decisions related to expansions, mergers, or acquisitions. A consistently high EBIT might indicate a good time to expand, while a declining EBIT could signal the need for strategic changes.
3. Budgeting and Forecasting: EBIT can be a starting point for budgeting processes, helping businesses set revenue and expense targets.
Ready to Optimize Your EBIT?
KEBS, a leading PSA software, offers tools that can help businesses optimize their EBIT. With KEBS resource management software, businesses can ensure optimal utilization of resources, leading to reduced operational costs and improved EBIT.
KEBS project management software ensures projects are completed on time and within budget, positively impacting EBIT. KEBS finance management software provides real-time insights into revenue and expenses, allowing businesses to make informed decisions that can enhance EBIT.
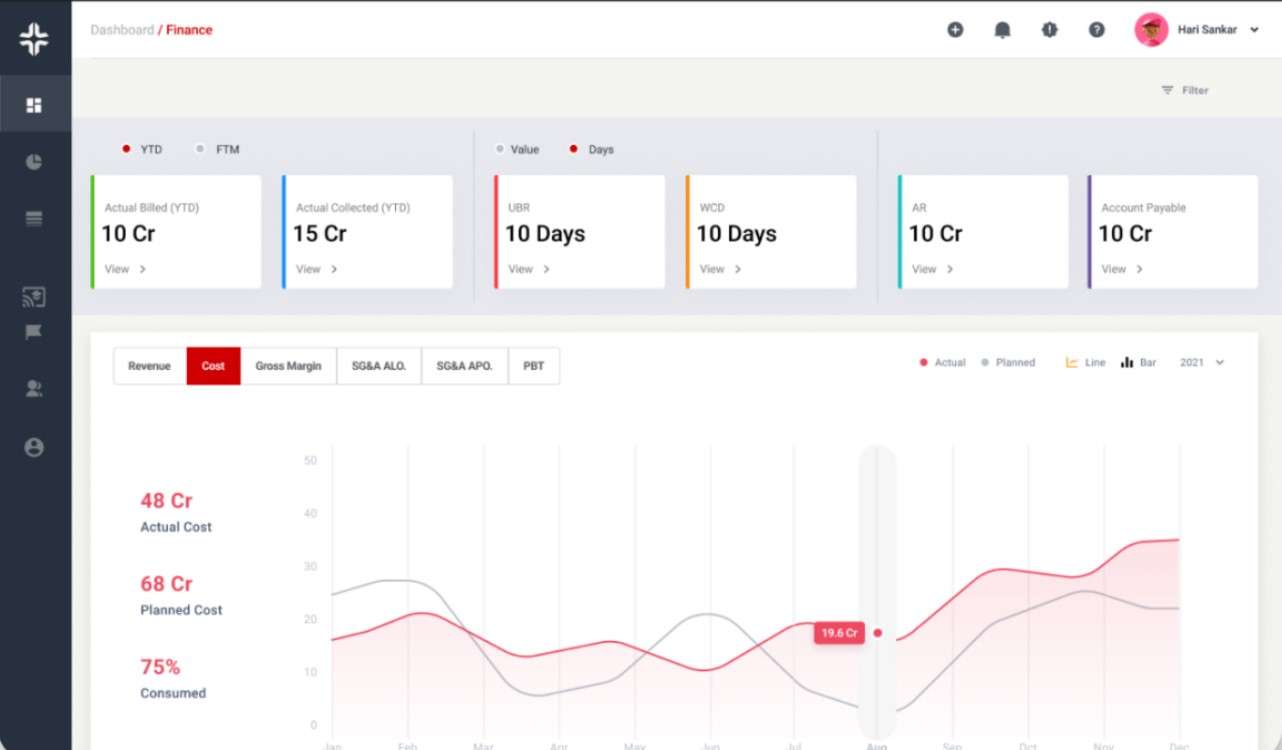
KEBS Finance Management
Ready to optimize your EBIT? Consider contacting KEBS or taking a demo to see how their suite of tools can elevate your business’s financial performance.



