Home » PSApedia
Net Operating Profit After Taxes
Gain Insights on Net Operating Profit After Taxes (NOPAT). Optimize Operations and Maximize Profitability.
What Is Net Operating Profit After Taxes?
Net Operating Profit After Taxes (NOPAT) is a financial metric indicating a company’s operational efficiency after accounting for taxes. It reflects the potential profitability of a company’s core operations, excluding the costs and benefits of its capital structure and tax impacts. NOPAT is crucial for understanding a company’s operational success, independent of its financing decisions.
It focuses solely on operating activities, excluding the impact of capital structure, interest, and non-operational income or expenses. Essentially, NOPAT showcases the earnings generated by a company’s core business activities before considering its financing decisions or tax implications.
Importance of NOPAT in Business
NOPAT is vital for investors and managers as it offers a clear view of a company’s operational performance. It’s particularly beneficial for comparison purposes, allowing stakeholders to assess the operational efficiency of companies regardless of their financing structures. For businesses, NOPAT helps in making strategic decisions, like expansions or cost-cutting measures.
1. Financial Health Indicator: NOPAT provides insight into the company’s operational profitability, excluding the effects of financing decisions and tax structures.
2. Investment Analysis: It helps investors evaluate the efficiency and profitability of a company’s operations without the influence of debt and tax strategies.
3. Performance Benchmarking: Companies often use NOPAT to compare performance across different time periods or with competitors.

Importance of Net Operating Profit After Taxes
How to calculate NOPAT?
NOPAT is calculated as Operating Income × (1 – Tax Rate). For example, if a company has an operating income of $200,000 and a corporate tax rate of 30%, NOPAT would be $140,000 ($200,000 × 70%). This calculation helps businesses and analysts in evaluating the company’s operational efficiency after taxes.
The formula to calculate NOPAT is straightforward:
NOPAT = Operating Income × (1−Tax Rate)
For example, if a company’s operating income is $1,000,000 and the tax rate is 25%, the calculation would be:
NOPAT=$1,000,000× (1−0.25) =$750,000
Difference Between NOPAT and other financial metrics
While NOPAT focuses on operational efficiency, net income includes all revenues and expenses, including financial costs, taxes, and one-time items. This difference is critical for accurate financial analysis, as NOPAT provides a purer measure of operational profitability.
One primary distinction lies in comparing NOPAT with Net Income. Net Income shows overall profitability after deducting expenses, taxes, interest, and non-operating costs. NOPAT focuses only on operational income before financing decisions.. This difference is crucial for investors and analysts to assess a company’s operational efficiency separately from its financial structure.
| Metric | Definition | Use / Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Net Operating Profit After Tax (NOPAT) | A company’s operating profit after deducting taxes | Evaluates the profitability of core operations, excluding tax effects |
| Net Income | Total profit after all expenses, including taxes | Reflects the overall profitability after accounting for all expenses |
| Revenue Growth Rate | Rate of increase in a company’s total revenue over a period | Indicates the growth trajectory and expansion of a company |
| Earnings Before Interest and Taxes (EBIT) | Operating profit before deducting interest and taxes | Measures operating profitability without considering financial structure |
Utilizing NOPAT in Business Analysis
NOPAT is used in financial metrics such as Cash Flow and Economic Value Added. It helps to determine a company’s value and its ability to generate cash. This helps analyze a company’s performance over time. It also helps compare the company’s performance to others. By removing the influence of financial structure, it creates a fair comparison.
NOPAT serves as a fundamental metric for various financial evaluations. Financial modeling extensively uses it, especially in calculating economic value added (EVA) or determining a company’s return on invested capital (ROIC). By focusing on operational earnings, NOPAT helps in assessing how effectively a company utilizes its resources to generate profits.
Ready to Optimize Your Financial Strategies?
Understanding and optimizing NOPAT is crucial for business success. For businesses seeking to enhance their operational efficiency and financial health,
KEBS, a Professional Services Automation (PSA) Software, offers robust tools to improve financial visibility and decision-making.
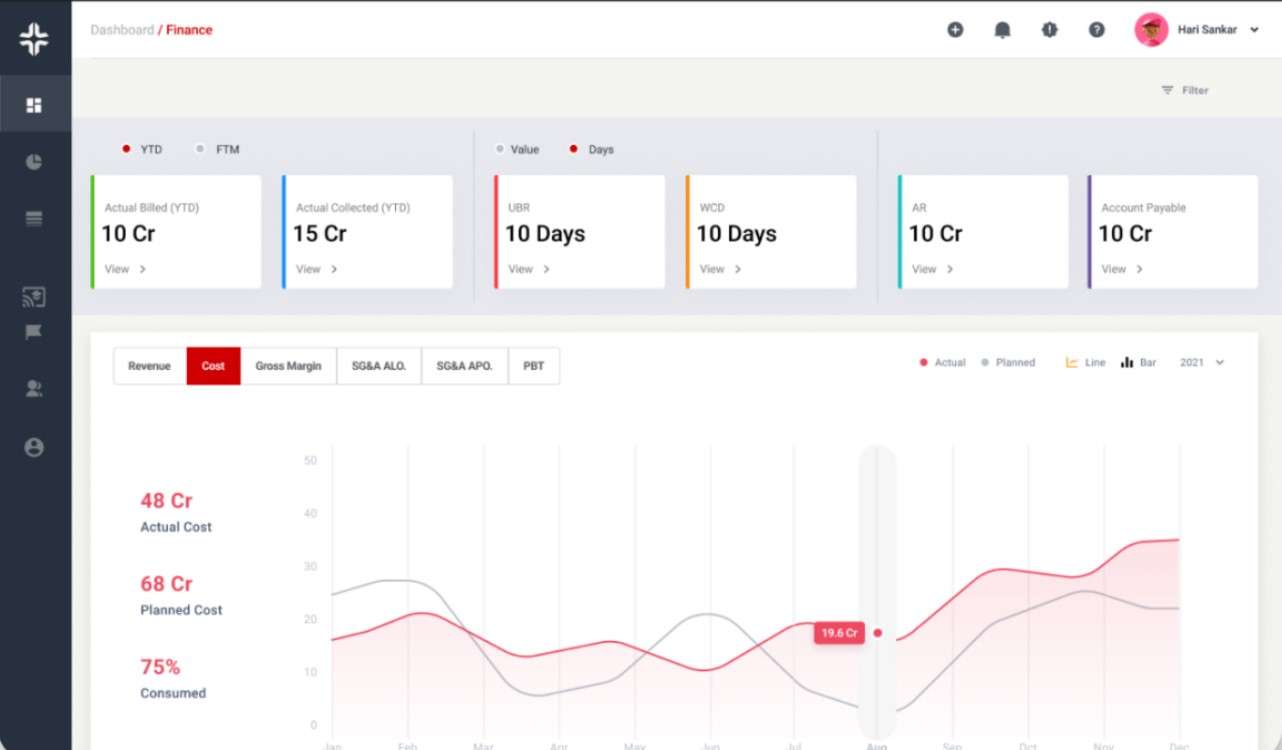
KEBS Finance Management
Explore KEBS and discover how its solutions can streamline your financial operations, from managing sales pipelines to automating timesheet billing. Ready to see KEBS in action? Schedule a demo or contact us today for personalized assistance.



