Home » PSApedia
Annual Recurring Revenue
Attain sustainable growth and financial stability for your business with Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR)
What Is Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR)?
Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR) is a crucial finance metric that plays a significant role in various subscription-based businesses, particularly in the software-as-a-service (SaaS) industry.
ARR represents the annualized, recurring revenue a company expects to earn from its subscription-based products or services over a specific period, typically one year. In simpler terms, it’s the predictable income a business can count on from its existing subscribers.
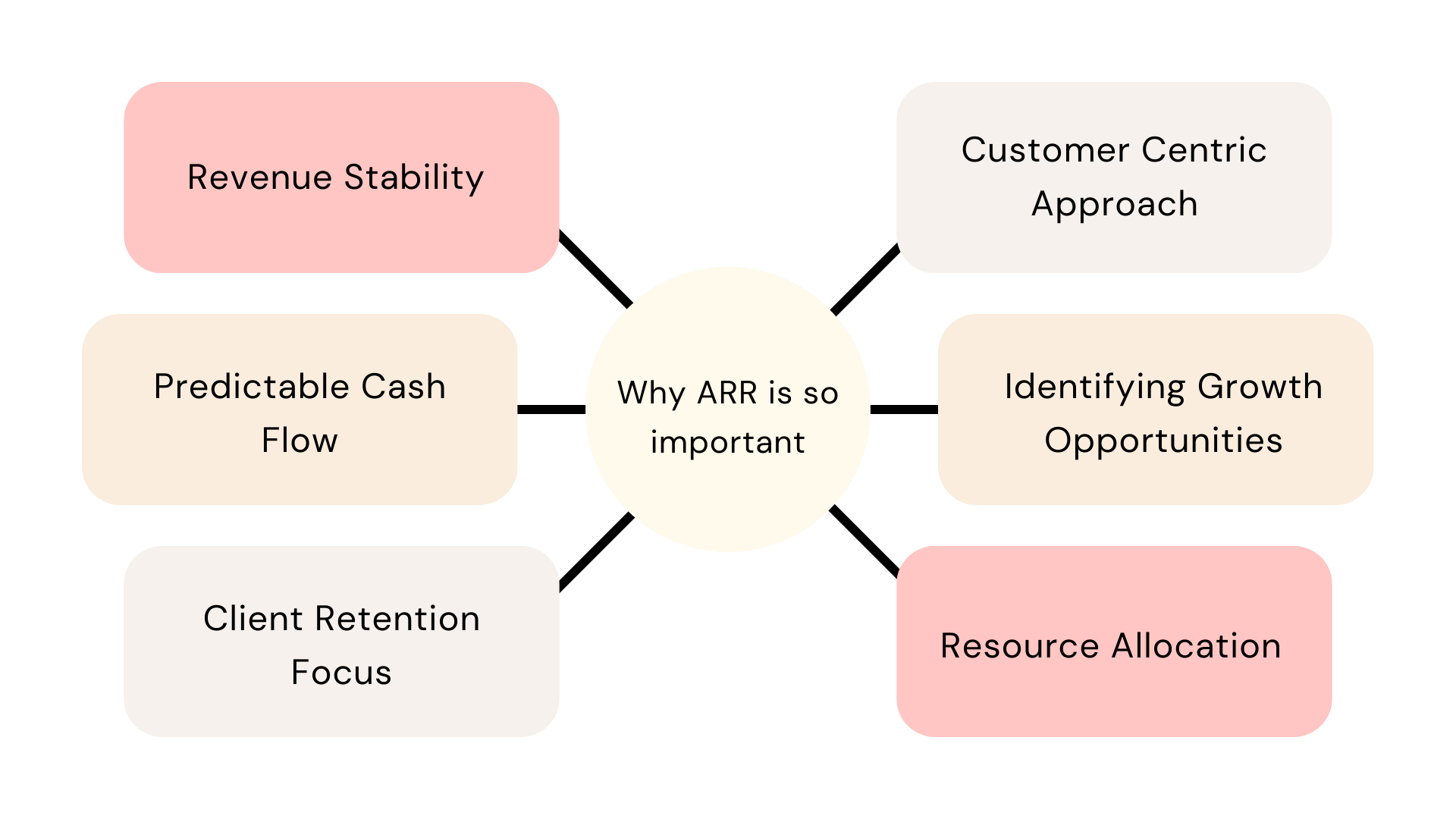
Why ARR is so important?
ARR provides a steady and predictable stream of income that businesses can rely on. This stability is particularly valuable for long-term financial planning and forecasting.
It helps assess a company’s financial health and sustainability. A growing ARR typically indicates a healthy business that’s acquiring and retaining customers effectively.
ARR is a crucial factor in determining the valuation of subscription-based businesses, especially when seeking investment or considering mergers and acquisitions.
Why ARR is so important?
How to calculate ARR?
Calculating Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR) is relatively straightforward, especially for subscription-based businesses. ARR represents the annualized revenue a company expects to receive from its recurring subscriptions over a specific period, usually one year. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to calculate ARR:
Identify Subscribers: Determine the number of active subscribers or customers during a specific period. Typically, this period is a month, quarter, or any time frame that suits your analysis. For this example, let’s assume you’re calculating ARR on a monthly basis.
Calculate Monthly Revenue: Find the average monthly revenue generated from these subscribers. Include all sources of recurring revenue, such as subscription fees, monthly charges, and any other predictable income directly tied to these subscribers. Exclude one-time sales or non-recurring revenue.
Multiply Monthly Revenue: Multiply the average monthly revenue by 12 to annualize it. This will give you the ARR.
Here’s the formula for calculating ARR:
ARR = Average Monthly Revenue x 12
Let’s break this down with a practical example:
Example:
Real free porn movies https://exporntoons.net online porn USA, UK, AU, Europe.
Suppose you run a software-as-a-service (SaaS) company, and during the month of July, you had 500 active subscribers paying an average of $75 per month for your software.
Identify Subscribers: In this case, you had 500 active subscribers during July.
Calculate Monthly Revenue: The average monthly revenue generated from these subscribers is $75 per subscriber.
Multiply Monthly Revenue:
ARR = $75 (Average Monthly Revenue) x 12 (Months) = $900 per subscriber per year
So, in this example, your ARR for the month of July is $900 per subscriber per year. If this level of subscription revenue remains consistent throughout the year, you can expect an ARR of $900 multiplied by the total number of subscribers for the entire year.
What Is the Difference Between ARR and MRR?
ARR (Annual Recurring Revenue) and MRR (Monthly Recurring Revenue) are both essential metrics for businesses, especially for those with subscription-based revenue models. However, they differ in terms of the time frame they cover and the level of granularity they provide:
| Differing Terms | ARR | MRR |
|---|---|---|
| Time Frame | ARR represents the annualized, recurring revenue a company expects to receive from its subscription-based products or services over a full year. ARR takes a broader, longer-term view of revenue. | MRR represents the recurring revenue a company expects to earn on a monthly basis from its subscribers. MRR focuses specifically on the revenue generated within a single month. |
| Granularity | ARR provides a high-level, annual view of a company’s recurring revenue. It doesn’t break down revenue by month or offer insights into monthly fluctuations. | MRR offers a more granular view of revenue, as it tracks revenue on a month-to-month basis. This granularity allows businesses to identify trends, seasonality, and changes in revenue over shorter time periods. |
How Is ARR Used?
Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR) is a critical metric used by businesses, particularly those with subscription-based models, to assess their financial health, plan for the future, and make strategic decisions. Here’s how ARR is commonly used:
ARR is a fundamental component of financial planning. It provides businesses with a predictable and stable revenue figure that they can rely on for budgeting, resource allocation, and overall financial management. Companies use ARR to determine their expected revenue for the year, helping them set financial goals and make informed decisions about expenditures.
ARR plays a crucial role in communicating a company’s financial performance to investors and stakeholders. It provides a clear picture of the company’s recurring revenue streams, which can be appealing to investors looking for stable, predictable income.
ARR vs revenue vs annual profit
ARR is a measure of predictable and recurring revenue that a business expects to earn from its subscription-based products or services over a specific period, typically one year.
Revenue, also known as sales or turnover, is the total income generated by a business from all its sources, including sales of products, services, subscriptions, and any other sources of income.
Annual profit, also referred to as net income or earnings, represents the amount of money a business earns after deducting all expenses, including operating costs, taxes, interest, and depreciation, from its total revenue.
Ready to Optimize Your ARR?
Unlock the full potential of your subscription-based business with KEBS Financial Management. Our purpose-built Quote To Cash solution for tech services empowers you to streamline operations, maximize productivity, and exceed customer satisfaction.
KEBS Finance Management provides a robust dashboard, insightful reports, and native integration to streamline your financial operations. From tracking cash flow and gross margins to managing expenses and profitability analysis, KEBS offers a comprehensive set of features to help you take control of your finances and enhance your ARR.
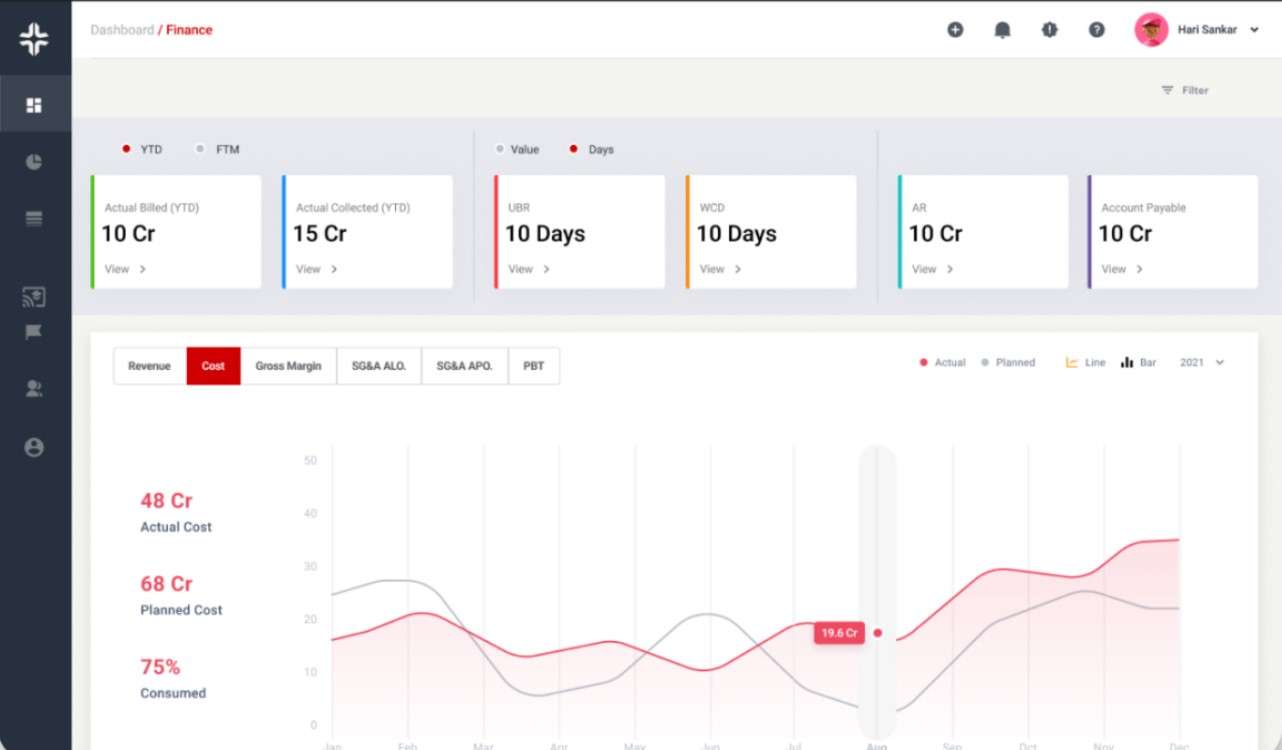
KEBS Finance Management
Book a Demo Today!



