Home » PSApedia
Variance Tracking
Enhance Business Decision-Making with Variance Tracking Tools. Explore Now!
What is Variance Tracking?
Variance tracking is the process of monitoring and analyzing differences between planned and actual outcomes, especially in terms of costs, resources, and time.
In the context of Professional Service Automation (PSA), it plays a pivotal role in ensuring projects are on track and resources are utilized optimally. By identifying discrepancies early, businesses can make informed decisions to steer projects back on course.
Importance of Variance Tracking
Variance tracking is crucial for several reasons:
1. Budget Control: It helps in identifying cost overruns and underutilized resources, ensuring that projects remain within budget.
2. Resource Allocation: By tracking variance, businesses can reallocate resources effectively, ensuring that no resource is overburdened or underutilized. This is particularly crucial in resource management.
3. Performance Analysis: Variance tracking provides insights into the performance of teams and individuals, aiding in evaluating resource performance and productivity in PSA.
4. Predictive Analysis: Historical variance data can be used to predict future project outcomes, aiding in better planning and forecasting.
Why ARR is so important?
How to Calculate Variance?
The basic formula for calculating variance is:
Variance = Actual Value − Planned Value
Example:
Suppose a project had a planned cost of $10,000 but actually cost $12,000. The variance would be:
(Variance) = $12,000 – $10,000 = $2,000
This indicates a negative variance of $2,000, meaning the project went over budget.
Variance Tracking vs Other Related Metrics
Variance tracking, while essential, is just one of many metrics used in PSA. For instance:
1. Variance vs Earned Value: While variance tracks the difference between planned and actual outcomes, earned value (EV) measures the value of work actually performed. Efficient project financial management often requires both metrics.
2. Variance vs Cost Performance Index (CPI): CPI is the ratio of earned value to actual costs. It gives a more comprehensive view of project performance than variance alone.
3. Variance vs Schedule Performance Index (SPI): SPI measures how efficiently the project team is using its time. While variance can indicate if a project is behind schedule
| Metric | Description | Purpose | Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| Variance Tracking | Measures the difference between planned and actual project performance. | Identify project deviations from the initial plan and budget, allowing for adjustments to be made. | Helps in budget control, project management, and resource allocation. |
| Earned Value Management (EVM) | Integrates scope, schedule, and cost performance to assess project health. | Evaluate project performance by comparing the value of work completed to the planned value. | Provides a holistic view of project progress and financial performance. |
| Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) | Sets of quantifiable metrics that reflect the overall success of the organization. | Monitor the overall health and performance of the professional services organization. | Assessing the company’s profitability, customer satisfaction, and employee productivity. |
How Variance Tracking is Used in PSA?
In PSA, variance tracking is used in various ways:
1. Project Management: Variance tracking helps project managers identify potential issues early on. Tools like Gantt charts can visually represent variances, making them easier to spot.
2. Financial Management: By tracking financial variances, businesses can ensure profitability. This is crucial in financial management in PSA.
3. Resource Management: Variance data can inform decisions about resource allocation, ensuring optimal utilization. This is evident in practices like resource allocation and forecasting in KEBS.
4. Client Communication: Sharing variance data with clients can foster transparency and trust. It’s a key aspect of enhancing client relationships.
Ready to Optimize Variance Tracking?
KEBS, a leading PSA software, offers robust tools for variance tracking. Here’s how KEBS can help. With KEBS, businesses can automate variance tracking, reducing manual errors and saving time. KEBS offers real-time reporting analytics, ensuring businesses have up-to-date variance data at their fingertips.
KEBS seamlessly integrates with other business systems, ensuring variance data is consistent across platforms. This integration is vital for holistic project management. Businesses can customize their KEBS dashboards to highlight key variance metrics, ensuring they’re always in the loop.
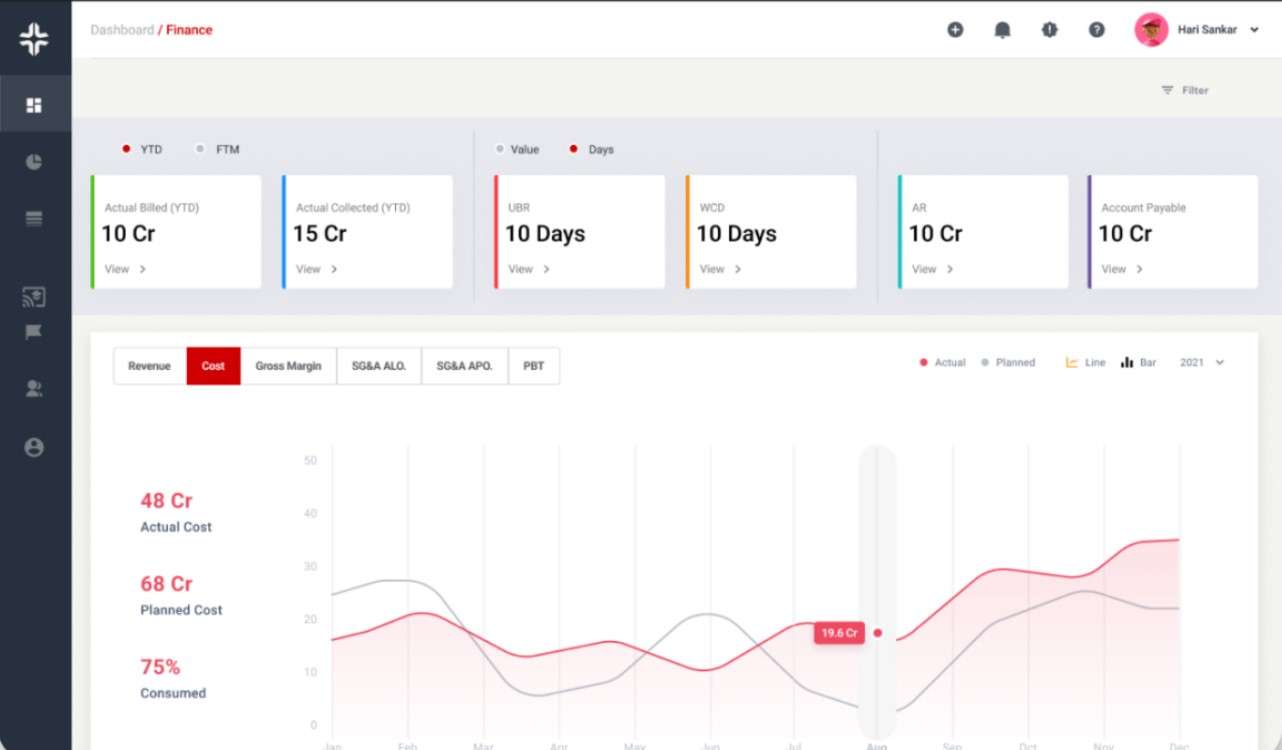
KEBS Finance Management
Ready to optimize your variance tracking? Contact us today or request a demo to see KEBS in action.



